To manage your costs effectively, you must understand the costs for all products you sell at a transaction level. These costs may also include nonmaterial costs such as freight, overhead, etc. This allows you to determine the actual cost associated with each product and therefore the profit that is recognized from its sale. It also allows you to accurately track the costs of those products you use internally.
Customer costing rules
- Costing included ( direct variable such as purchase cost, import tax cost, insurance cost and forex difference incurred from the time company receive a copy of vendor invoice and the time the bank decides to grant a loan to the Company; and semi-variable cost
- Updated Average Cost to be propagated to all branches (or at the Company level) at the end of the day. Account Posting happens only in HQ.
- Average Costing is re-calculated daily based on every Receipt from ( Purchase (i.e. receipt from goods in transit or receipt from local purchase); or Goods returned from sales, or Exchange stock at a different price or different label
Note: In case of recalculating COGS, opening stock value is closing qty of the previous day * WAC of the previous day
Cost Type
Cost Type allows you to distinguish different costs to track. These are user-defined and may include Current, Future, History, etc. When defining your Accounting Schema(s) you will select a Cost Type.
In the Accounting Schema, we previously defined the rules or parameters for posting documents and transactions. We will also define the Costing Method, Costing Type and Costing Level. NGERP will calculate all Material Cost Elements that you have defined but it is the Costing Method selected in the Accounting Schema that will be used when posting the accounting consequences for each document.
Business Rules
- The customer uses default costing type
UI /Report Layout
- Enter a Name for this Cost Type
- Add a Description and Comment/Help if desired
- Select the Active checkbox to indicate that this Cost Type is Active
Cost Element
Cost Elements allow you to define the different items that will comprise your costs. You can define any number of Cost Elements, keeping in mind that some will have to be manually maintained.
A number of Cost Elements are calculated by the system and should not be modified (other than to change the Name) once they are added. These include Average Invoice, Average PO, Last Invoice Price, Last PO Price, LIFO, and FIFO. Each has a Cost Element Type of Material (as it is associated with the movement of an item) and the associated Costing Method.
Business Rules
- The customer uses the Average invoice costing method to calculate the weighted average cost
- The customer has handling fee cost elements. It is in charge of selling expense
UI /Report Layout
- Enter a Name for this Cost Element and optionally, enter a Description if desired
- Select the Active checkbox to indicate that this Cost Element is active
- Select a Cost Element Type of Burden (M Overhead), Resource or Outside Planning to categorize this Cost
Product Cost
There are a number of additional costs you may want to include for specific products. This can include but are not limited to Handling, Overhead and Acquisition Costs. These costs may be a fixed amount or a percentage of other costs. To use additional costs, they must first be defined as Cost Element.
Note: If Standard Costing is being used, then no additional Costs will be included in the Cost
The customer uses standard cost meaning that there is no mark up against the actual cost.
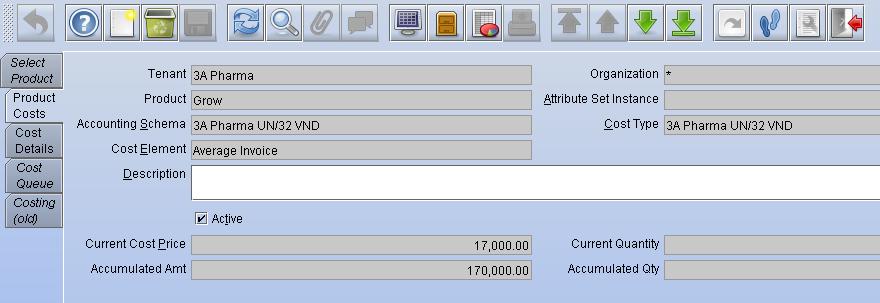
Enter either a Current Cost Price or Percent to be used for the Handling fee Cost. If you enter a Current Cost Price that amount is added to the other Costs to determine the final cost for each unit. If a Percent is entered, it is multiplied by the sum of all other costs and added to the other costs to determine the final cost.
For example, assume that the Costing Method is Average Invoice. The Grow has a Cost Element of Average Invoice = 65.00 and an Acquisition Cost Element of 6.00.
A Handling Fee Cost Element is added for 10.00. The final cost would be 65.00 + 6.00 + 10.00 = 81.00
If a Handling Fee Cost Element is added for 10 percent, the final cost would be (65.00 + 6.00) * 1.10 = 78.10.
All Cost Prices are added before the Percent is applied.
UI /Report Layout
Landed Cost
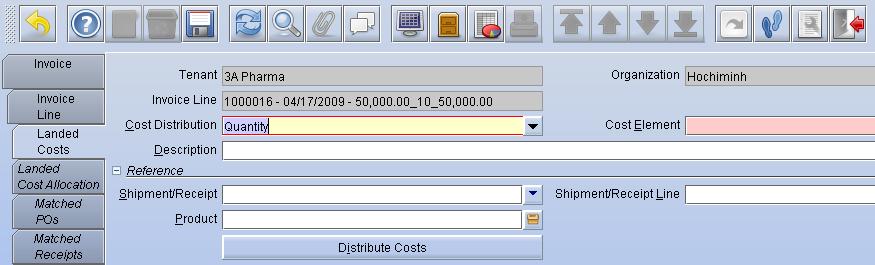
There may be a situation when you receive an Invoice for additional charges for Material Receipts which have already been invoiced. These may include Freight charges, Handling Charges or any other fees. If you want to allocate these additional costs to the Product or Products received then you would create a Landed Cost Invoice.
Here, the 100.00 Cost was allocated to the 3 lines based on Quantity. The calculation used for the first line is (2 / 7) * 100 = 28.57.
This process is done for each line and if necessary the largest amount is adjusted to account for rounding differences.
Currently, the Customer not using landed for cost calculation.
UI /Report Layout
Average cost calculation
The customer calculates the cost using the average cost method. The following costs are included for cost calculation
1. Cost and Freight (C&F cost)
2. Import Duty
3. Insurance
Business Rules
- Costing method is Perpetual Weighted Average Cost method
- Insurance and Import duty will be entered manually, no system calculation
- The VAT is not included for cost calculation
- Import Duty will be line level
- Insurance will be at line level
Formula
Average cost = (CIF + Import Duty)/ Line quantity.
| SKU | Quantity | CNF $ | Insurance $ | Import Duty $ |
| Line 1 – Grow | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Line 2 – Sure | 10 | 15 | 1 | 1.5 |
Average cost for Line1 CIF = CNF + Insurance = 10+1 A = CIF+ Import Duty = 11+1 = 12 Average Cost = A/line ordered quantity = 12/10 = 1.2 Average cost for Line1 CIF = CNF + Insurance = 15+1=16 A = CIF+ Import Duty = 16+ 1.5 = 17.5 Average Cost = A/line ordered quantity = 17.5/10 = 1.75
Product Cost Report
The product cost report lists the product costs for the product, cost type, and cost element.
UI /Report Layout
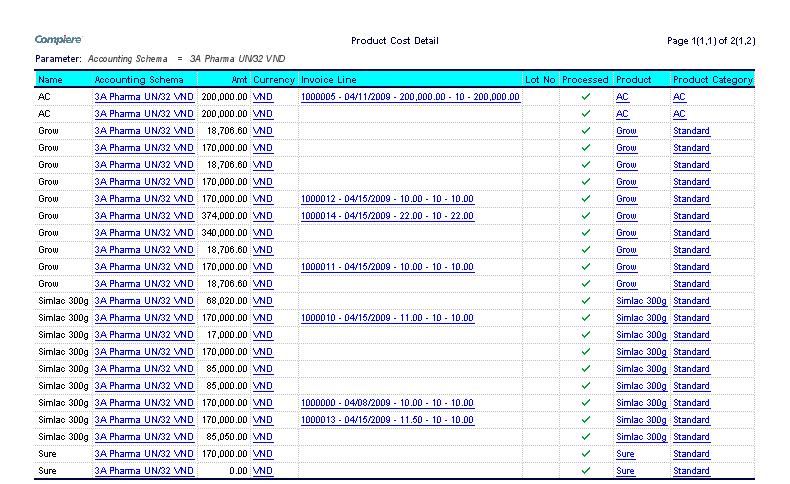
Product Cost Detail
The product cost detail report lists the product cost with individual invoice cost allocation.
UI /Report Layout
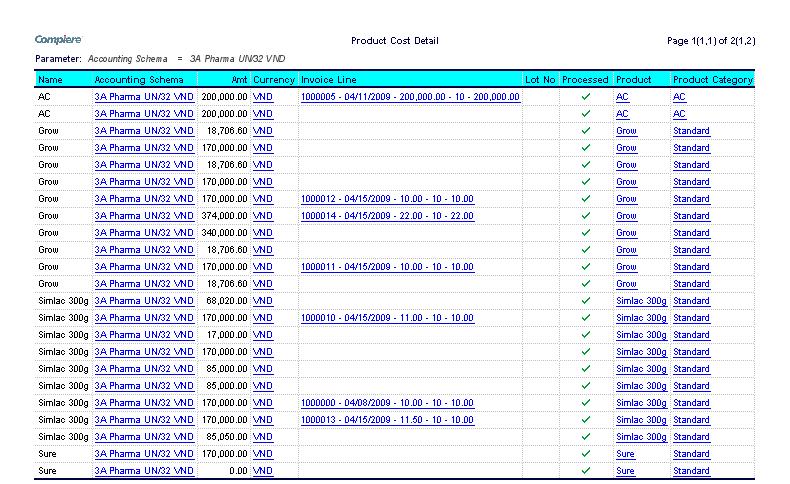
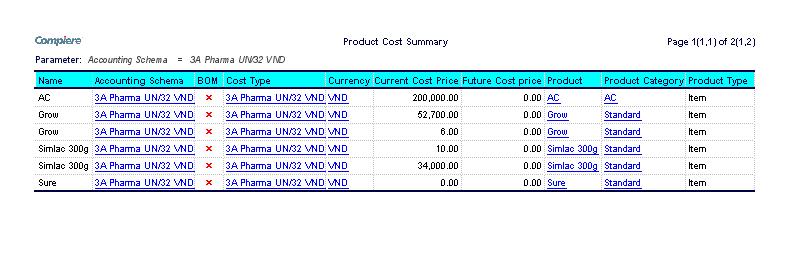
Product Cost Summary
The product cost summary report lists the summarized product costs for the product.
UI /Report Layout
COGS Calculation
This used to calculate the COGS for the whole company.
| Stock in | Branch Transfer In/(out) | Stock out | Closing stock | ||
| Qty | Qty | Qty | Qty | Value | |
| Opening balance | 10 | 1,000 | |||
| 2/1/2009 | 10 | 20 | 2,080 | ||
| 3/1/2009 | 20 | 40 | 3,911 | ||
| 4/1/2009 | 30 | 70 | 7,467 | ||
| 5/1/2009 | (20) | 50 | 5,333 | ||
| 6/1/2009 | (10) | 40 | 4,267 | ||
| 7/1/2009 | 20 | 60 | 6,753 | ||
| 8/1/2009 | (25) | 35 | 3,939 | ||
| 9/1/2009 | (5) | 30 | 3,376 | ||
| Total | 80 | (20) | 40 | 30 | 3,376 |
Business Rules
- Calculated every day for the whole company
To be recalculated if there is a purchase or goods returned from sales or exchange stock at dif price or dif label. (In case of recalculating, opening stock value is closing qty of the previous day * WAC of the previous day)

