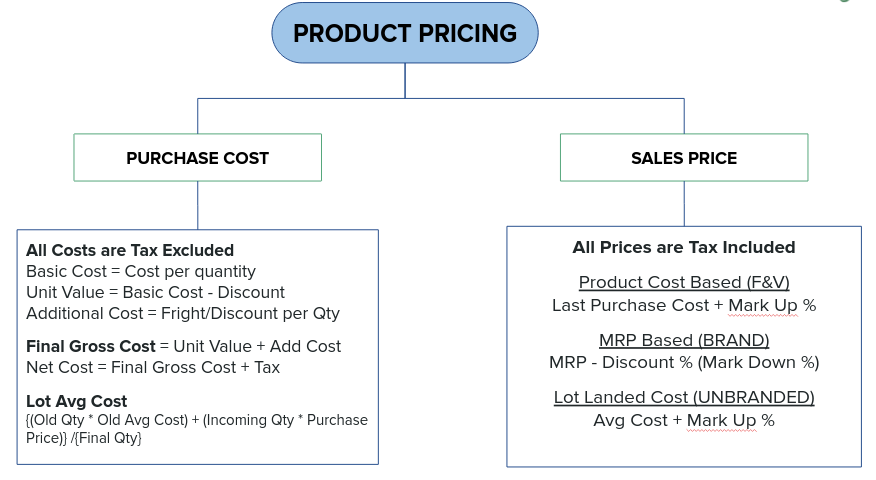
Product Pricing
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy for a Retail Product
Pricing is a critical factor in retail success. Choosing the right pricing model can maximize profits, attract customers, and ensure competitiveness.
Indian retail pricing is a mix of cost structures, taxes, and competitive strategies. Whether you run a small store, an e-commerce business, or a large retail chain, understanding these components helps in optimizing profits while staying compliant. Below is a breakdown of key retail pricing models, their advantages, disadvantages, and best use cases.
1. Key Components of Retail Pricing in India
A. Cost Price (CP)
- The price at which a retailer purchases the product from the manufacturer or wholesaler.
- Includes:
- Purchase Cost (with/without discount)
- Transportation & Logistics
- Import Duties (if applicable)
B. Wholesale Price (WP)
- The price at which distributors sell to retailers.
- Typically includes a 10-30% markup over the cost price.
C. Maximum Retail Price (MRP)
- The highest price a retailer can charge, as per Indian law.
- Must be printed on all packaged products.
- Includes:
- Manufacturer’s Cost + Profit
- Distributor/Wholesaler Margin
- Retailer Margin
- Goods & Services Tax (GST)
D. Selling Price (SP)
- The final price at which the product is sold to customers.
- Can be equal to or lower than MRP (but never higher).
- Retailers may offer discounts below MRP.
2. Pricing Strategies Used by Odoo Retail (Indian Retailers)
A. Cost -Plus Pricing (Markup Pricing)
- Formula: Selling Price = Cost Price + Profit Margin (%)
- Common in Grocery stores & small retailers.
B. Discount Pricing (Markdown Pricing)
- Prices are set based on discounts below MRP.
- Used for Branded products (Hamam, Gold Winner) in supermarkets.
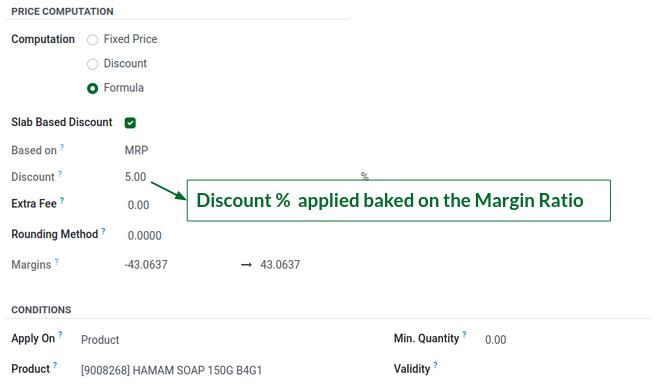
C. Dynamic Pricing (Margin Based)
- Prices change based on common margin slabs
- Discount applied on MRP
- Example: 1%-10% margin gets 2% Discount on MRP. 20%-40% margin gets 10% Discount on MRP.
D. Psychological Pricing
- Prices like ₹99, ₹499 to make products seem cheaper.
- Common in fashion, FMCG, and electronics.
E. Promotional Pricing
- Festival Sales (Diwali, Big Billion Days)
- Buy 1 Get 1 Free (B1G1), Cashback Offers
- Example: 50 % off on Specific Category/Brands/Products
F. Bill Value-Based Pricing
- Promotional strategy where a discount is applied automatically if the total bill value crosses a certain threshold.
- Example: Get 5% off on orders above ₹2,000
3. Taxes Impacting Retail Pricing in India
A.Taxes in Retail Pricing
- GST slabs:
- 0% – Essentials (milk, fresh food)
- 5% – Branded food items
- 12% – Processed food, cosmetics
- 18% – Electronics, furniture
- 28% – Luxury goods (with additional cess if applicable)
- GST is included in the MRP, not added separately at the counter.
Pricing Challenges
✔ Price Sensitivity – Indian consumers prefer discounts & low-cost options.
✔ GST Compliance – Different tax slabs affect final pricing.
✔ Competition from E-commerce – Online discounts pressure offline retailers.
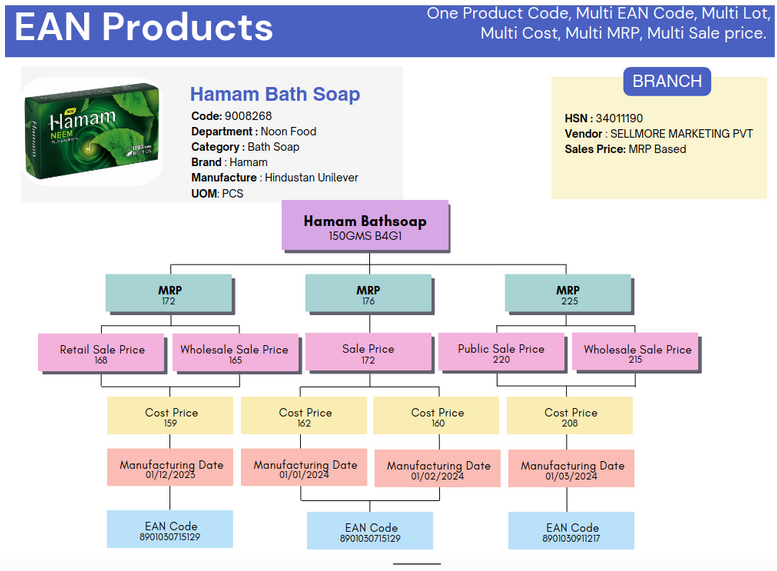
4. Odoo Retail Price list
A. Multiple Prices per product
Assign different set of prices to each Companies and assign to Customers.
Example: Public Pricelist, WholeSale Pricelist, Membership Pricelist
B. Advanced Price rules (discounts, formulas)
Price rules and apply discounts, margins, and roundings
Example: 2 % Discount from MRP, 10% Markup from Cost
C. POS Terminal / Company Based
Set different price lists specific to company or branch in POS terminal.
5. Screenshots
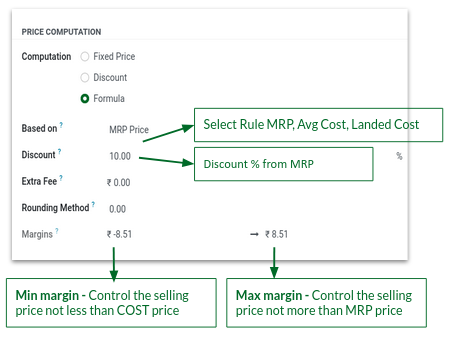
A. Selling Price – MRP Based (Branded Products)
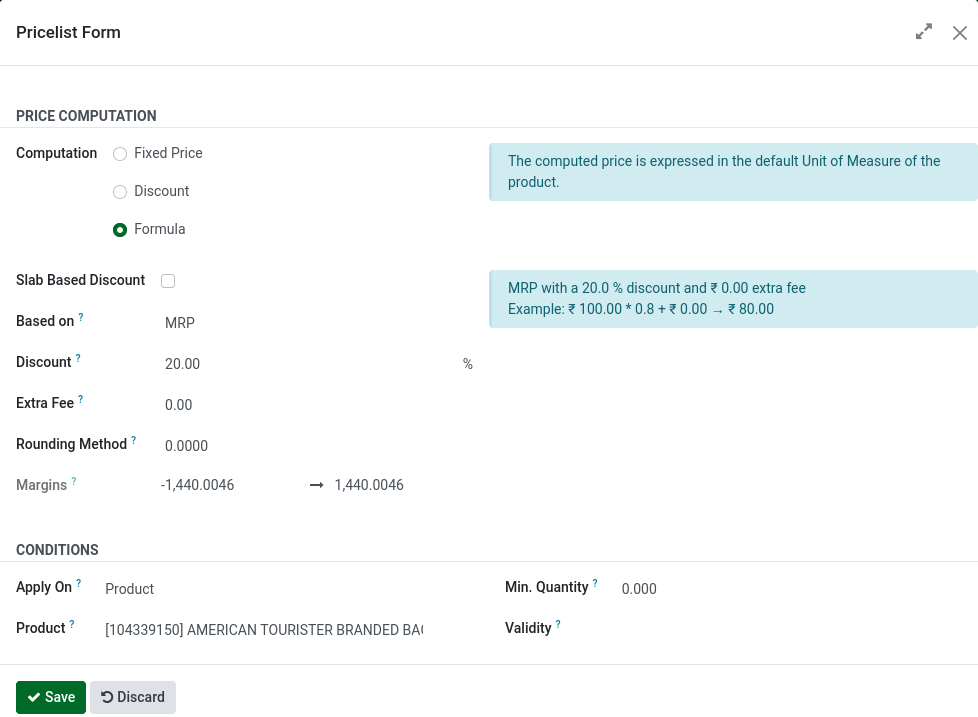
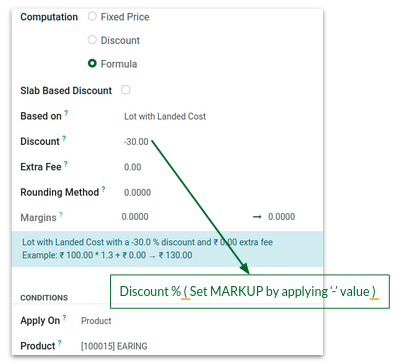
B. Selling Price – Lot Cost Based (Unbranded Products)
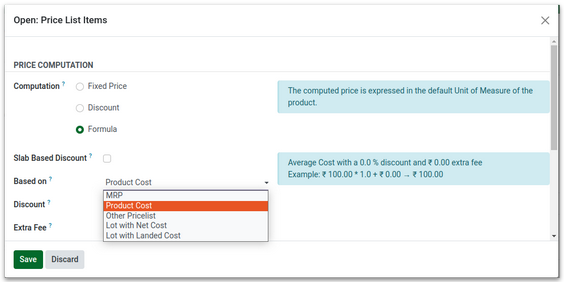
C.Selling Price – Product Cost (F&V)
D.Selling Price – Slab Based (Margin Ratio)
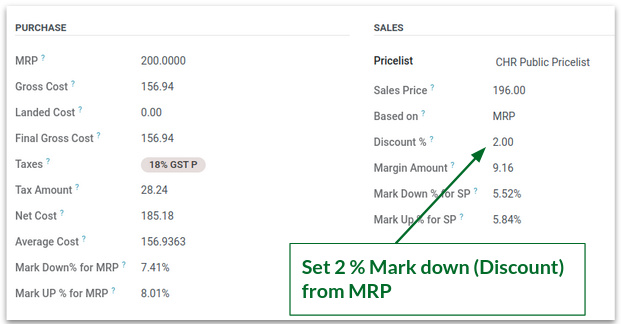
6.Price Info – Example
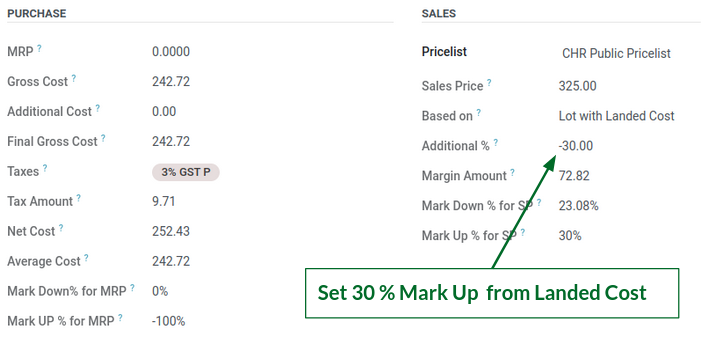
Set 2% Mark Down from MRP
Set 30% Mark up from Landed Cost