Odoo 18 eCommerce
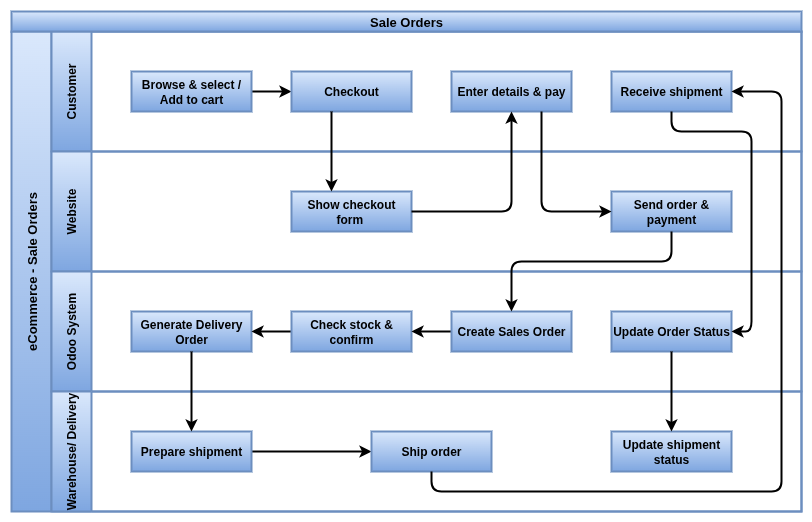
Odoo eCommerce is an online shop platform built inside Odoo. It allows businesses to create and manage their own website shop without needing extra software. From designing the website, adding products, setting prices, handling taxes, to receiving online payments everything can be done in one place. Customers can easily browse products, place orders, make payments and track deliveries online.
The best part is that Odoo eCommerce is directly connected with Sales, Inventory, Accounting and CRM. This means stock updates, invoicing and customer follow-ups happen automatically without duplicate work. Businesses can sell to both individuals (B2C) and companies (B2B). It also supports different payment gateways, shipping methods, coupons and promotions.
In simple words, Odoo eCommerce helps any business run a professional online shop that is easy to manage, looks modern, and keeps all records in sync with the rest of the business.
Process Flow

Payment Process Flow

Key Feature
Drag-and-drop website builder with mobile-responsive and SEO-optimized themes.
- Support for physical, digital, and subscription products.
- Product variants with multiple attributes (size, color, fabric, etc.).
- Bulk import of products and images via CSV/Excel.
- Multi-level navigation menus and mega menus.
- Advanced search with dynamic filters (price, size, color, extras).
- User-friendly shopping cart with save and resume functionality.
- Guest checkout and registered user checkout options.
- Automatic tax calculation based on customer location.
- Integration with major payment gateways (PayPal, Stripe, etc.) supporting secure and PCI-compliant payments.
- Supports partial payments, pay-on-delivery, and recurring payments for subscriptions.
- Multiple delivery methods with fixed, free, or rule-based charges.
- Real-time shipping rates via carriers like UPS, FedEx, DHL with API integration.
- In-store pickup (Click & Collect) support configured with warehouse settings.
- Delivery options filtered by customer’s shipping country.
- Real-time inventory tracking with barcode support.
- Multi-warehouse and drop-shipping capabilities.
- Automated order management including fulfillment, invoicing, and returns.
- Customer portal for order tracking, returns, and invoice access.
- Wishlist and product review system.
- AI-powered personalized product recommendations.
- Discount codes, loyalty programs, and abandoned cart recovery.
- Integrated email marketing and SEO tools.
- Comprehensive sales, customer behavior, inventory, and fulfillment reports.
Screenshot
Kanban View

List View
Product Add to Cart

Share with Social media Options
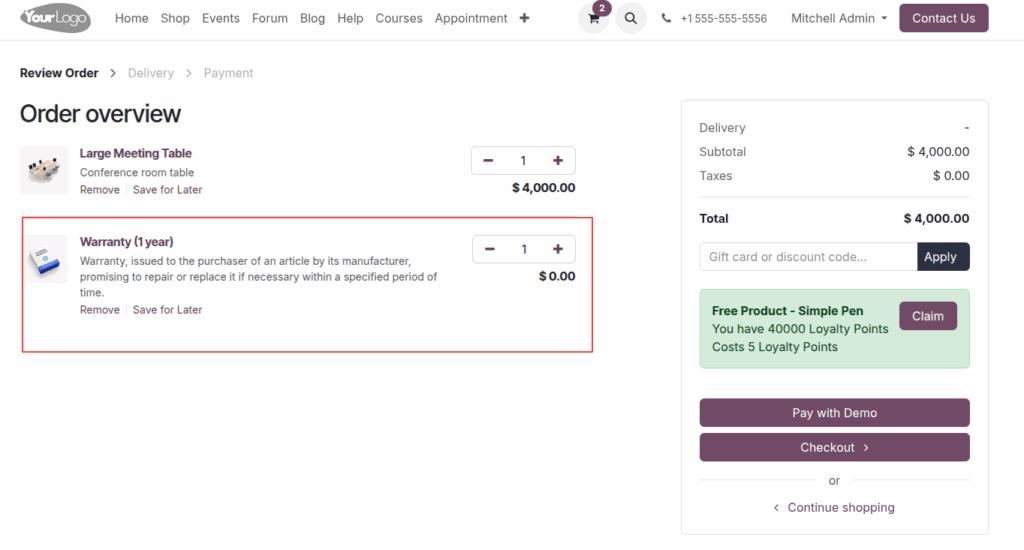
Cart
Product With Warranty
Product Without Warranty
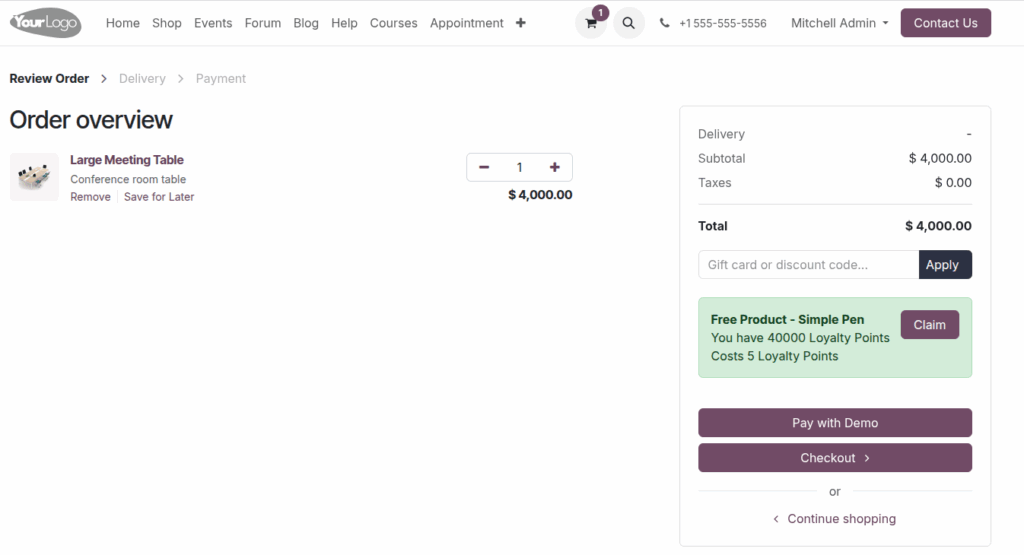
Payment Screen
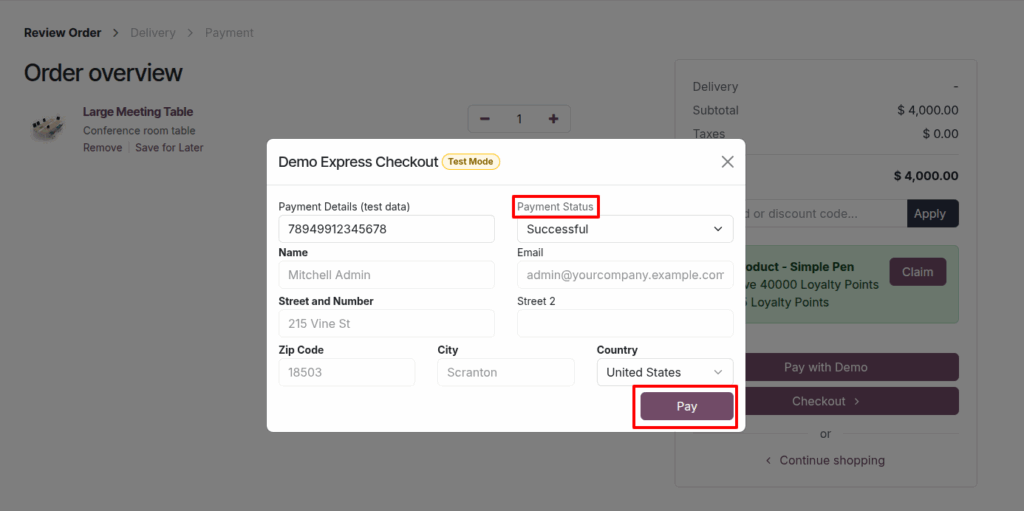
eCommerce Configuration Management
This involves setting up how customers pay and receive their orders by managing payment providers, payment methods, and delivery options.
- Payment Providers
- Payment Methods
- Delivery Methods
eCommerce Orders Management
This covers handling all aspects of customer orders, including processing orders, managing unpaid orders and abandoned carts, and keeping track of customer details.
- Orders
- Unpaid Orders
- Abandoned Carts
- Customers
eCommerce Product Management
This area focuses on managing the product catalog, including products, pricing, categories, attributes, product combinations, tags, and special labels to organize and promote products effectively.
- Product
- Pricelists
- eCommerce Categories
- Attributes
- Combo Choices
- Product Ribbons
eCommerce Loyalty Management
- Discount & Loyalty
- Gift cards & eWallet
Dashboard
- eCommerce Dashboard
eCommerce Configuration Management
Payment Providers
eCommerce, payment providers are services (like Stripe, PayPal, Adyen) integrated into the website checkout to allow online transactions. These are configured under the Website or Accounting apps.
Process Flow

Business Rules
- Each payment provider in Odoo must have a unique internal identifier and must be activated to be usable on the website.
- Providers must be set to “Published” to appear on the eCommerce checkout page.
- Only one mode (Test or Production) can be active at a time for each provider.
- A payment provider must be linked with valid API keys and credentials provided by the service.
- When a payment is successfully processed, Odoo automatically confirms the sale order and marks the payment as paid.
- If the payment fails, the transaction is logged and the order remains in quotation or cancelled state.
- Each provider can be restricted by country, currency, and website, using configuration filters.
- Odoo supports provider-specific callbacks (e.g., webhook URLs) to validate and confirm payment status.
- Admin users must manually enable and test the provider before using it in a live environment.
- Payment providers are tied to companies; in multi-company setups, they are not shared between companies.
Screenshot

Payment Methods
Payment methods in Odoo 18 are the available options customers can use via a provider, such as Visa, MasterCard, or Apple Pay. These appear as individual options during the website checkout process
Process Flow
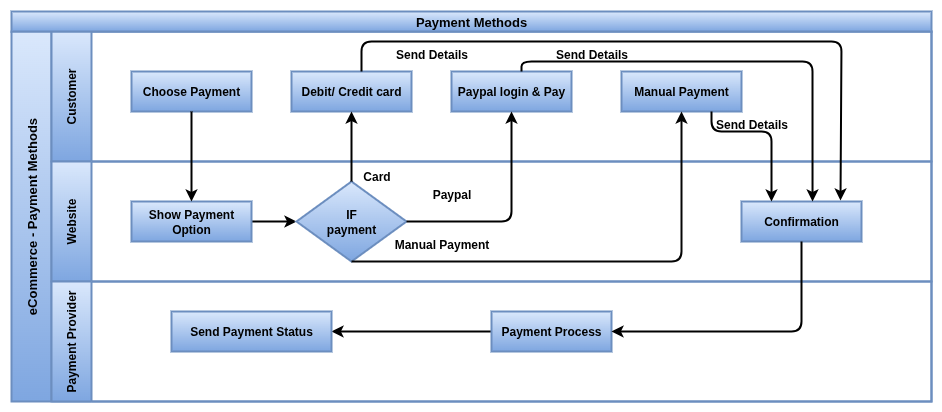
Business Rules
- Payment methods cannot be created manually; they are automatically synced based on the provider’s capabilities.
- Only methods that are marked as “Available” and supported by the provider will show on the checkout page.
- The order and visibility of payment methods are controlled by the sequence number set in the provider configuration.
- Odoo uses branding (icons and labels) from the provider to visually represent each method during checkout.
- Tokenization (saving payment info) is available only if the provider supports it and the feature is enabled in Odoo.
- Payment methods are linked to a specific payment provider; they cannot be used independently.
- When a tokenized method is selected, Odoo uses secure tokens—no sensitive card data is stored locally.
- Payment method availability may vary depending on the currency, country, or website language.
- If no payment methods are available for the selected provider, the checkout page will show an error.
- Payment methods are not configurable individually in the backend; they inherit rules from their provider.
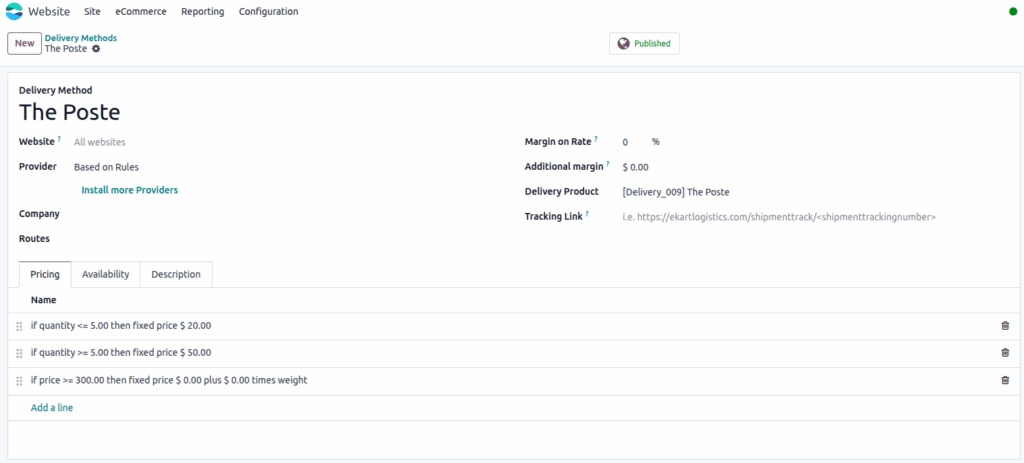
Delivery Methods
Delivery methods in eCommerce define how the order is shipped to the customer. They are shown at the shipping step during the website checkout.
Process Flow
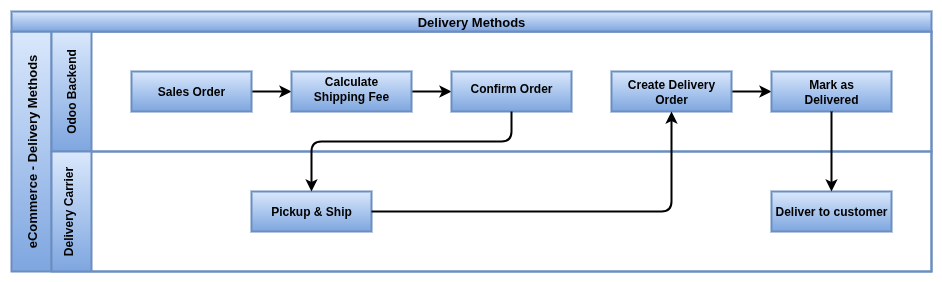
Business Rules
- Delivery methods must be enabled and published in the Website app to appear during checkout.
- Each delivery method must have a unique name, pricing rule, and delivery product assigned.
- Delivery charges can be fixed, free, or computed based on rules (e.g., price, weight, destination).
- Live rate providers (e.g., UPS, FedEx) must have valid API credentials and configured service levels.
- In-store pickup (Click & Collect) is supported if the delivery method is configured with a pickup warehouse.
- Only delivery methods available for the customer’s shipping country will be shown at checkout.
- If no delivery method is available based on configured filters, Odoo will block checkout until resolved.
- Delivery margins can be added as fixed amounts or percentage-based markups in the method settings.
- Delivery methods trigger the automatic creation of Delivery Orders in the Inventory app once the sale is confirmed.
- Users must have access to Website or Inventory settings to configure delivery methods.
Screenshot
eCommerce Orders Management
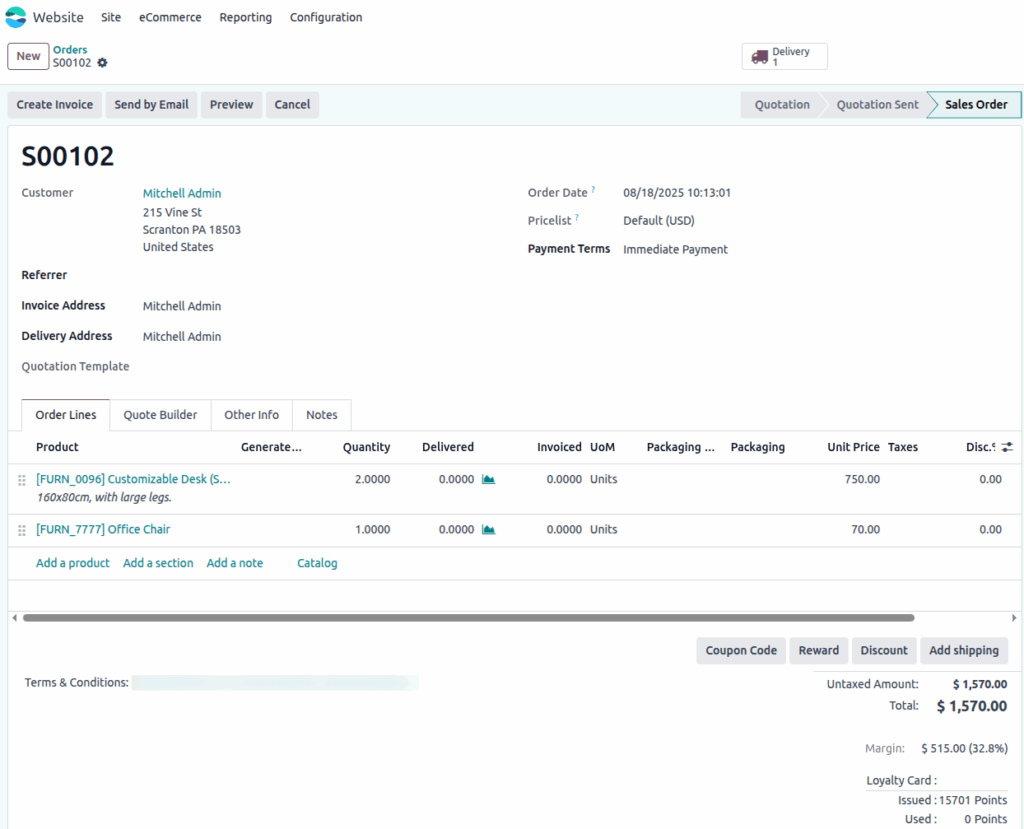
Orders
In Odoo Enterprise eCommerce, an order is created when a customer completes the checkout process on the website. Odoo generates a Sales Quotation, and upon successful payment or manual confirmation, it becomes a Sales Order.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- When a customer places an order on the website, Odoo creates a sales order automatically in the system.
- If the customer pays successfully online (e.g. via card, PayPal), the order is confirmed and processed immediately.
- If the customer chooses a manual payment method (like bank transfer or pay later), the order stays in “draft” until payment is received.
- If the payment fails or is canceled, the order is saved but marked as unpaid and not processed.
- Unpaid orders do not ship and are not invoiced until payment is completed or confirmed by an admin.
- Website orders include all chosen items, delivery charges, taxes, and customer contact information.
- Customers who check out without logging in are saved as new customers using the name and email they entered.
- After a successful order, the customer receives an automatic confirmation email with their order details.
- Customers can log in to their account anytime to view order history, invoices, and delivery status.
- Admins can see all orders from the website, including which ones are unpaid, paid, or failed.
- In businesses with multiple websites or branches, orders go to the correct team or company based on the site the customer used.
- Only authorized staff can confirm, cancel, or update orders placed through the website.
Screenshot
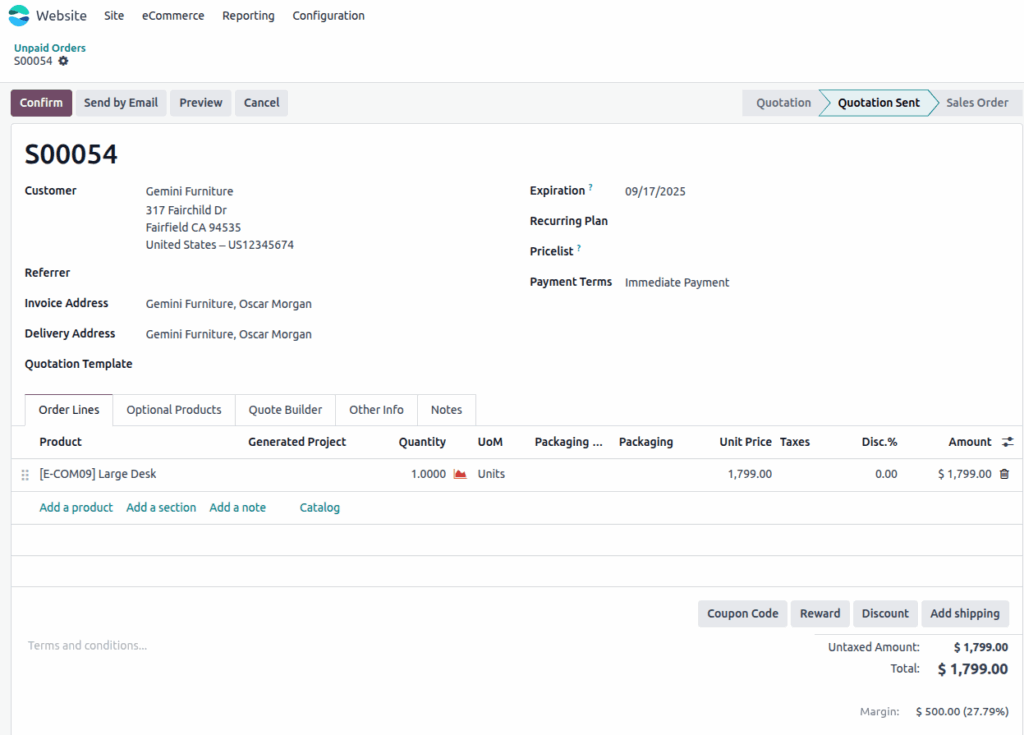
Unpaid Orders
Unpaid orders are quotations where the checkout was completed, but payment was not successful or pending (e.g., wire transfer, failed card, or manual approval).
Process Flow

Business Rules
- Odoo keeps unpaid orders in quotation (draft) status until payment is completed or manually confirmed.
- Orders using manual payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, pay later) remain unpaid until reconciled.
- Incomplete or failed online payments (e.g., declined cards) result in unpaid orders with failed transaction logs.
- Admin users can manually confirm unpaid orders and log payments from the backend.
- In multi-company setups, unpaid orders are isolated per company and must be confirmed separately.
- Unpaid orders do not trigger delivery or invoicing until confirmed.
- Unpaid orders can be filtered from Website → Orders → Unpaid Orders, or through Sales filters.
- Accounting reconciliation of unpaid orders happens only once a payment journal entry is posted.
- Odoo can send automated follow-up emails to remind customers to complete payment (via Marketing Automation).
- Access to unpaid order management is restricted to users with Sales or Accounting rights.
Screenshot
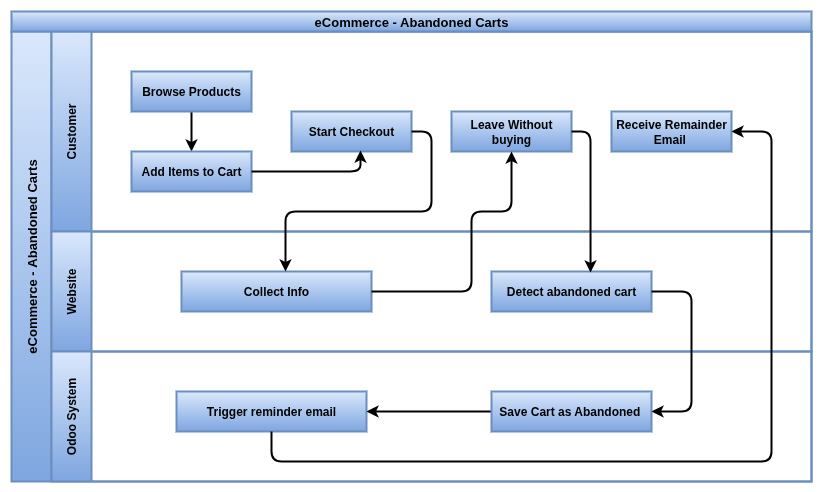
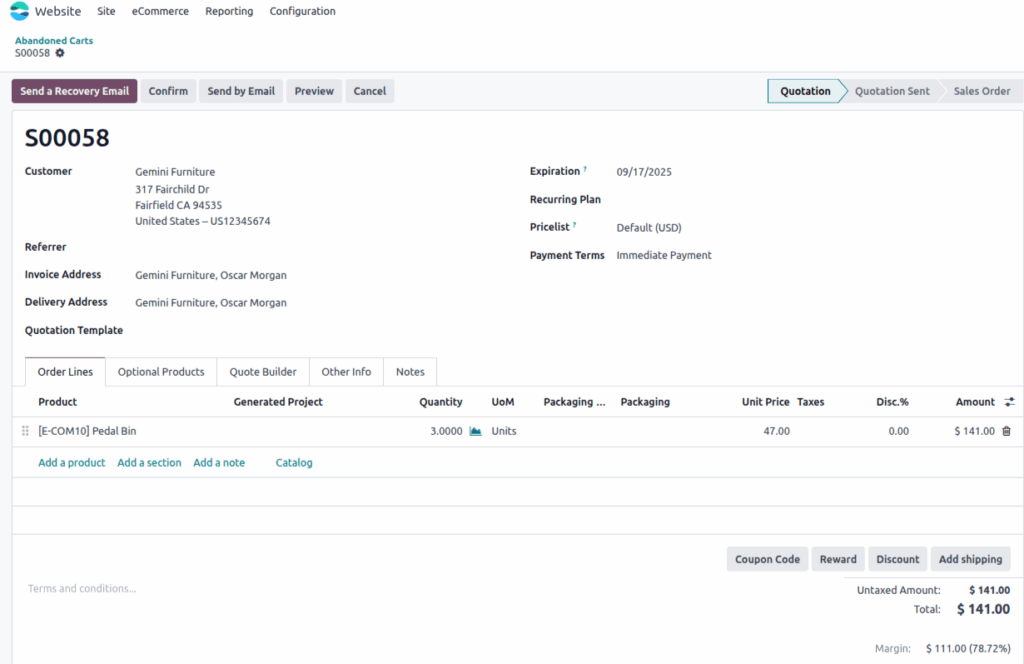
Abandoned Carts
Abandoned carts in Odoo are partially completed checkouts where the customer added items but did not finish the order. These are tracked in real-time and linked to visitor sessions.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Abandoned carts are created when a visitor adds items to the cart but does not complete the checkout.
- The system uses browser cookies or visitor IDs to identify abandoned carts per user session.
- Carts are stored with product, quantity, price, and cart timestamp but no delivery/payment info.
- If the visitor logs in or registers, the cart is linked to their contact record.
- Abandoned carts are accessible from Website → Orders → Abandoned Carts.
- Odoo Enterprise allows automated recovery emails using Email Marketing or Marketing Automation.
- Recovery emails include dynamic links that restore the customer’s cart on the next visit.
- Cart expiration time can be customized in developer settings or overridden using custom modules.
- Reporting dashboards show cart abandonment rates and recovery success per campaign.
Screenshot
Customers
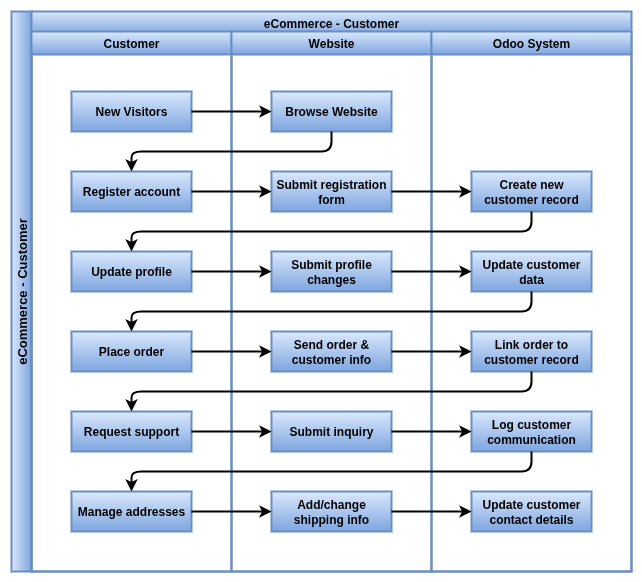
In Odoo 18 Enterprise, customers are either registered portal users or anonymous guests who make purchases via the website. Odoo automatically creates a contact for every transaction.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- A customer is created in the Contacts module each time a new user completes a checkout (guest or registered).
- Registered users are assigned Portal access and can log in to view orders, invoices, and deliveries.
- Guest checkouts still create a customer record with available billing/shipping details and email.
- Duplicate detection uses email address and name to prevent multiple entries for the same person.
- Contacts created through eCommerce are marked with website customer tags for segmentation.
- The Customer Portal is automatically available to all customers with a valid user account and email.
- Portal access can be revoked or upgraded by admin users via user access rights.
- Each customer is linked to their complete Sales, Invoice, and Delivery history.
- Customers can manage their addresses, track orders, and download invoices via the portal.
- Multi-website setups maintain isolated customer views unless cross-company contact sharing is enabled.
Screenshot
eCommerce Product managements
Products
In Odoo 18 eCommerce, products are the core items listed for sale on the website. Each product is stored in the Sales and Inventory modules and made visible through website configuration.
Process Flow
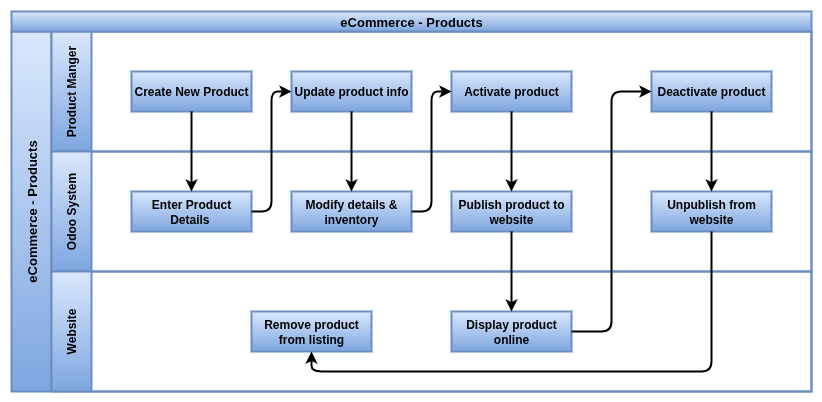
Business Rules
- Products must be marked as “Can be Sold” and “Published on Website” to appear in the eCommerce storefront.
- Each product must have a unique internal reference or SKU to avoid duplication.
- A product’s Sales Price, tax configuration, and unit of measure must be set for checkout and invoicing.
- Products can be configured as Storable, Consumable, or Service, impacting stock management.
- The product’s description in the Sales tab appears on the product detail page by default.
- Only published products are indexable by Odoo’s website search and filters.
- Products can have optional SEO metadata, custom URLs, and social sharing settings via the Website tab.
- Inventory rules such as routes (e.g., Buy, Dropship) must be set to manage fulfillment.
- Product images are resized and optimized automatically when uploaded via the backend.
- In multi-website mode, products can be restricted per website and priced independently.
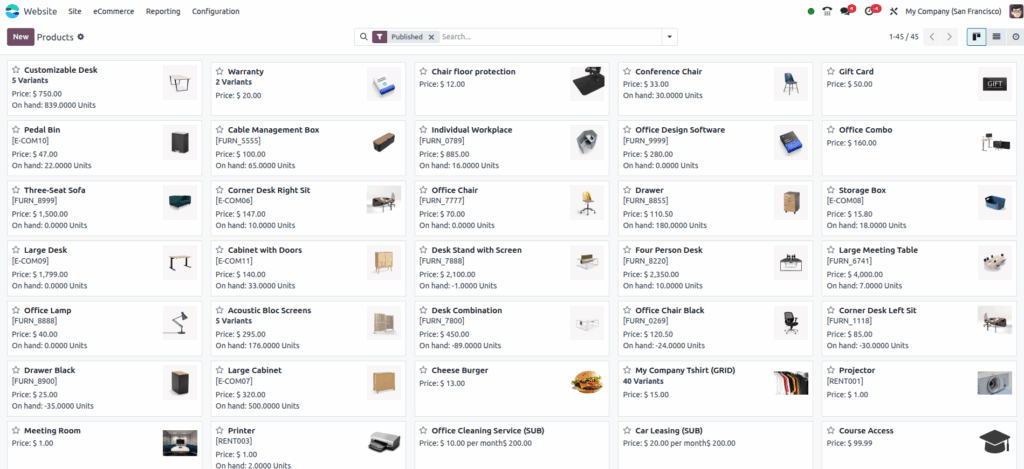
Screenshot
Price lists
Price lists define dynamic product pricing rules based on conditions such as customer groups, currencies, minimum quantities, or dates.
Process Flow
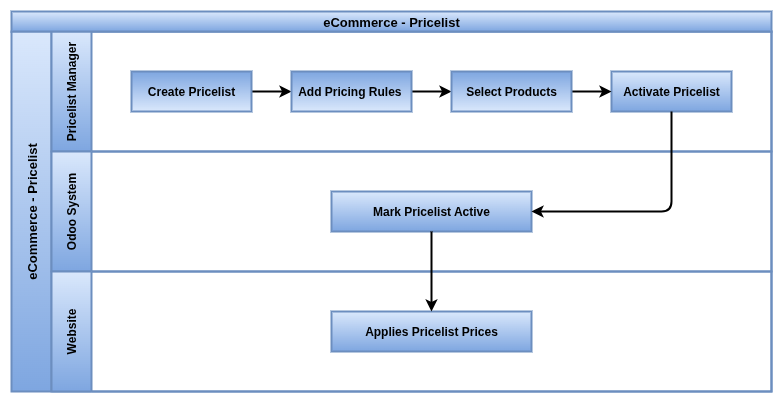
Business Rules
- Pricelists must be enabled under Website Settings to apply customer-specific pricing on the eCommerce site.
- Each pricelist must have a unique name and pricing rule structure (fixed, formula, or discount-based).
- Customers are assigned a default pricelist; it can also be dynamically selected during login or checkout.
- Website users only see product prices based on the pricelist assigned to them.
- Multiple currencies are supported, but each pricelist must be configured with a currency and proper rounding rules.
- Pricelists can apply globally or be restricted by country, language, customer tags, or product categories.
- Promotion rules (e.g., Buy X Get Y) must be defined using pricelist rules or discounts under Sales Promotions.
- Pricelists can show crossed-out original prices for public discounts when properly configured.
- Time-bound pricelists support start/end dates to handle temporary campaigns or seasonal offers.
- Pricelists are respected across all sales channels (website, POS, backend orders).
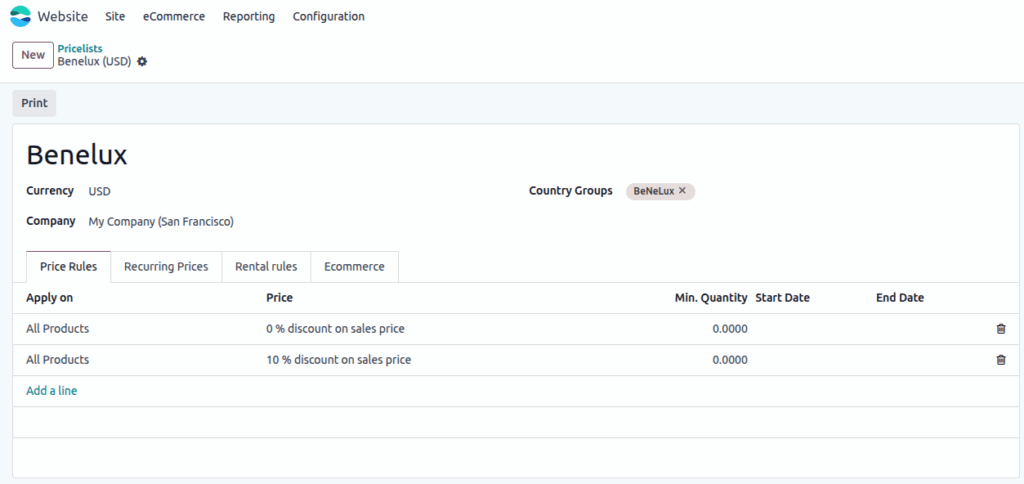
Screenshot
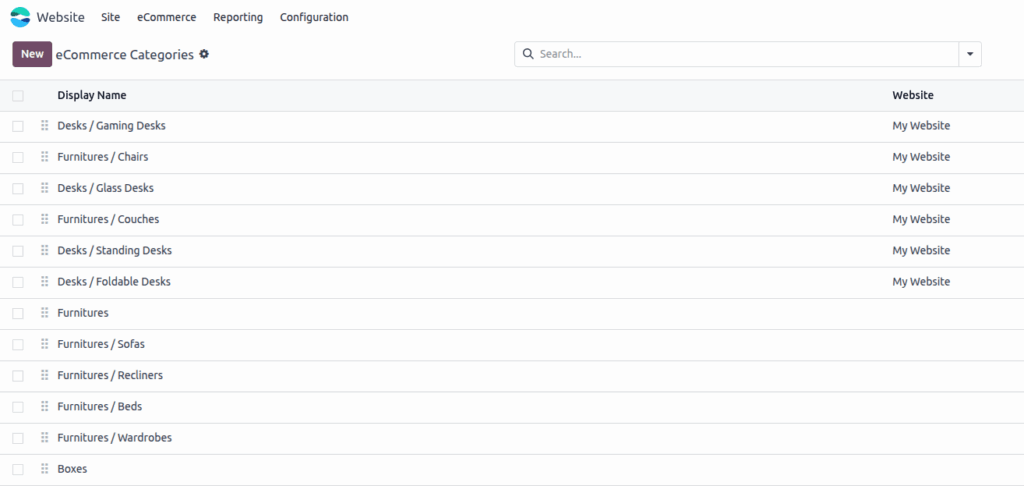
eCommerce Categories
eCommerce Categories organize products on the website into logical groupings, affecting navigation and product discovery.
Process Flow
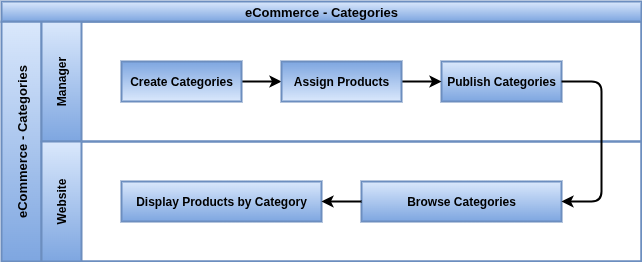
Business Rules
- eCommerce categories are separate from internal product categories used for accounting and inventory.
- A product must be explicitly assigned to at least one eCommerce category to be browsable via the storefront.
- Categories can be nested to form multi-level menus (e.g., Clothing → Men → Shirts).
- Each category can have a description, banner image, and SEO metadata to improve the landing page.
- A category can be hidden from the menu while still accessible via direct URL or links.
- The menu structure is automatically updated based on category hierarchy in Website > Shop > Categories.
- Categories support multi-website visibility rules, allowing different catalogs for each website.
- When filtering on the shop page, only products assigned to that category are shown.
- Admins can manually control sort order of categories and products using sequence fields.
- Deleting a category does not delete the products inside; they simply lose the navigation path.
Screenshot
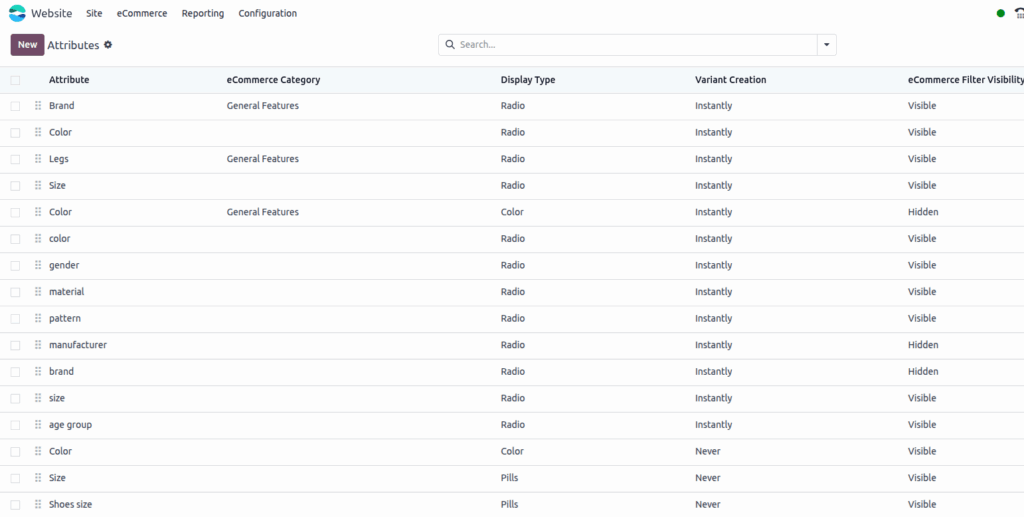
Attributes
Attributes are used to define product variants (e.g., Color, Size) and allow customers to choose options at checkout.
Process Flow
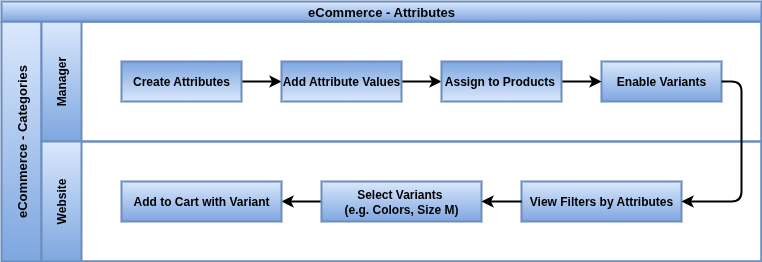
Business Rules
- Attributes must be defined under Sales → Products → Attributes before assigning them to products.
- Each attribute can be used to create variants automatically or act as a custom option.
- Only attributes marked as “Used in eCommerce” will appear on the product page dropdowns or selectors.
- Attribute values must be unique within each attribute and cannot be reused across types.
- The combination of attributes creates product variants, each with its own stock and price if needed.
- Website users can select variants directly, and Odoo updates the image and price dynamically (Ajax-based).
- Attributes can have display types (radio, color, dropdown) for better UX in eCommerce settings.
- Admins can control if a variant has a different image, barcode, or cost, even if the parent product is the same.
- Variants are listed in the backend with a parent-child relationship to the main product template.
- Attributes cannot be modified if variants already exist; instead, variants must be re-generated.
Screenshot
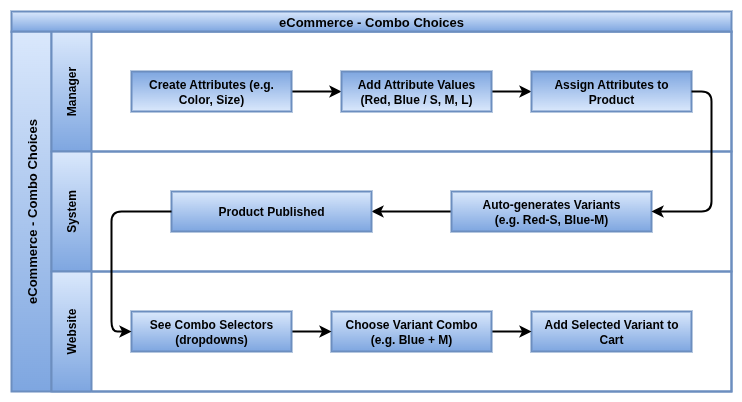
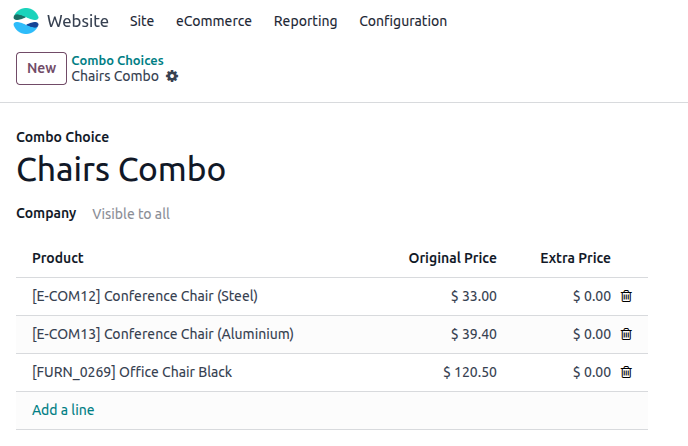
Combo Choices
Combo Choices (aka Optional Products or Cross-sells) are add-on items shown during or after the product is added to the cart.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Combo products are configured in the product’s Sales tab under “Optional Products.”
- These appear during checkout or after adding to cart as upsell recommendations.
- Each combo item must be an active, published product in the system.
- Combo suggestions are not mandatory and can be skipped by the customer.
- The system displays the combo products with price, name, and optional image preview.
- Optional products cannot have conflicting taxes or incompatible units of measure.
- Discounted combos require additional pricelist or promotion rule configuration.
- Optional products work only for eCommerce and do not apply in POS or backend sales by default.
- Combo logic is limited to one level; nested combos are not supported out-of-the-box.
- Optional product selection is saved to the order line and linked to the main product reference.
Screenshot
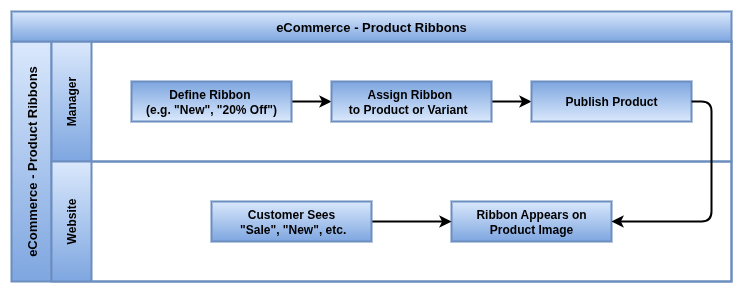
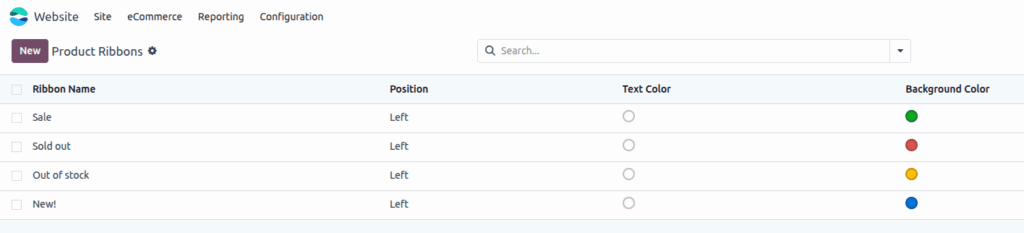
Product Ribbons
Product Ribbons are visual badges displayed on product images (e.g., “New”, “Sale”, “Sold Out”,”Out of the stock”).
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Ribbons are configured under Website > Products > Ribbons and assigned per product.
- Only one ribbon can be displayed per product at a time.
- Ribbons can be assigned manually or conditionally via automated rules (custom module or studio).
- The ribbon text and color can be customized to match brand style (e.g., red for “Limited Offer”).
- Ribbon visibility is frontend only and does not affect stock, pricing, or backend logic.
- Ribbons are shown in both grid and product detail views when the product is published.
- Ribbons are template-driven, so design can be modified using Odoo Studio or theme XML.
- Ribbons support translation for multilingual websites.
- Admins can prioritize ribbons by setting sequence to control which ribbon appears first.
- Ribbon logic can be extended using computed fields or automated actions for campaign timing.
Screenshot
Customers Loyalty Management
Discount & Loyalty
Overview
Discount & Loyalty features help to drive customer engagement and increase sales by offering discounts, reward points, and promotional incentives on the eCommerce platform. Customers can receive discounts via promo codes or automatically based on configured rules, and accumulate loyalty points that can be redeemed for future purchases
Process Flow
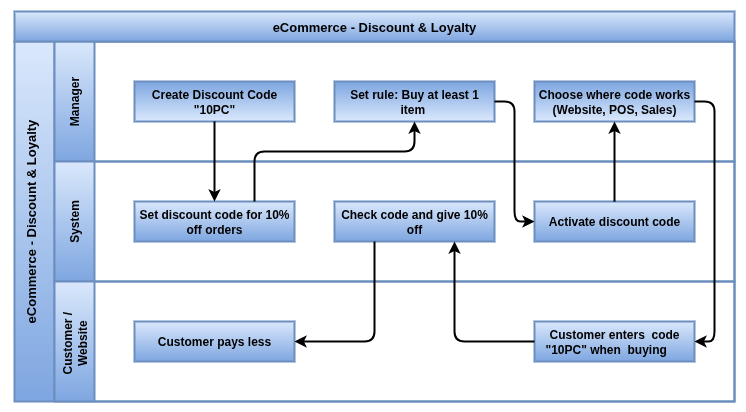
Business Rules
- Discounts can be applied via promo codes or automatic promotions during checkout.
- Promo codes have restrictions such as expiry date, usage limits, minimum order value, and customer eligibility.
- Loyalty points are earned based on customer spending or specific product purchases.
- Customers can redeem loyalty points partially or fully to reduce the order total.
- Loyalty point balances and redemption history are visible in the customer portal.
- Discounts and loyalty redemption are applied before taxes and shipping fees.
- Promotions can be targeted by product categories, customer groups, or websites.
- Discounts and loyalty redemption can be configured to be mutually exclusive or combinable.
- All discount and loyalty transactions are logged for auditing and reporting.
- Discounts are reflected in sales orders, invoices, and customer communications.
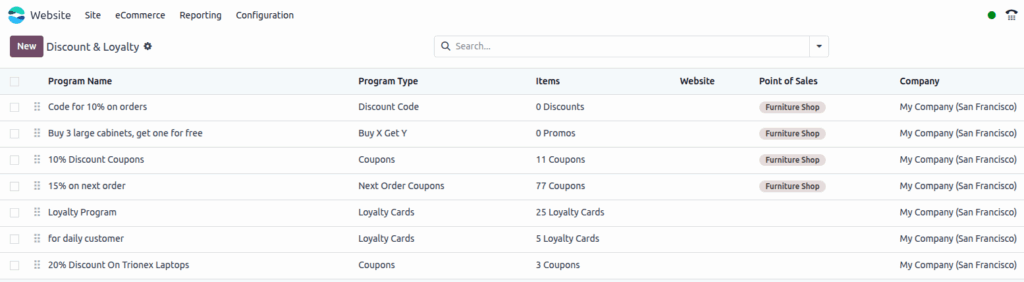
Screenshot
Gift Cards & eWallet
Overview
Gift Cards and eWallet provide flexible prepaid payment options for customers. Gift cards are virtual products with unique codes that customers can purchase and redeem on the eCommerce website. eWallet acts as a stored credit balance where refunds and rewards can be deposited for future use.
Process Flow
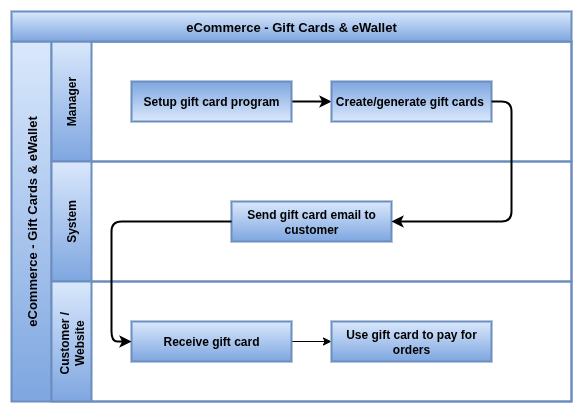
Business Rules
- Gift cards are sold as products with unique codes generated upon purchase.
- Gift card codes are emailed to customers and can be redeemed during checkout.
- Gift card balances are tracked and reduced as they are used.
- eWallet acts as a prepaid wallet credited with refunds, loyalty rewards, or manual deposits.
- Customers can use eWallet balances fully or partially during checkout payments.
- Gift cards and eWallet balances are non-transferable and tied to individual customer accounts.
- Expiry dates for gift cards and eWallet credits are enforced according to configuration.
- Admins can manually adjust balances and monitor all transactions.
- Gift card and eWallet transactions integrate with accounting for proper financial tracking.
- Gift card codes cannot be reused once fully redeemed.
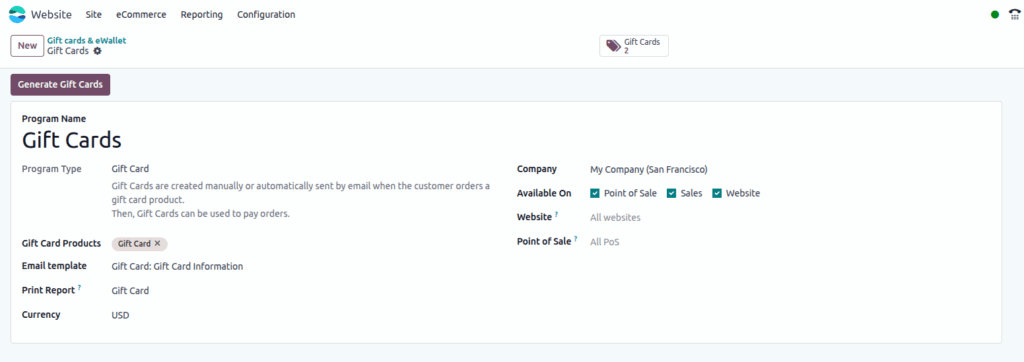
Screenshot
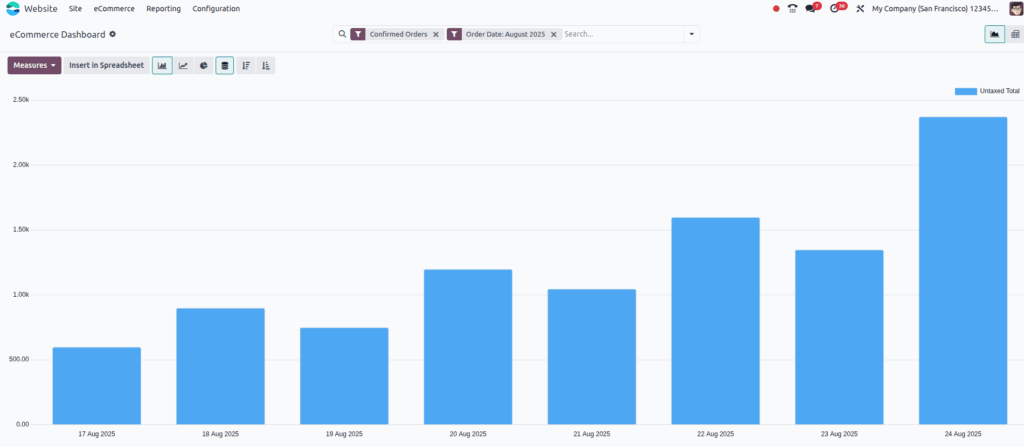
eCommerce Dashboard
Overview
Odoo 18 Enterprise Edition provides a robust reporting system for monitoring and analyzing eCommerce sales performance. The reporting tools aggregate sales data by various dimensions (product, category, time period) and display key performance metrics such as margin, quantity invoiced, untaxed total, and sales volume. Users can interact with the data through different views, apply filters, compare periods, and export reports for deeper analysis. This system enables businesses to track sales trends, optimize product offerings, and make informed decisions to improve overall eCommerce performance.
Business Rules
- Access to the eCommerce reporting dashboard is restricted to users with appropriate permissions, typically sales managers and analysts.
- Sales data is automatically collected and aggregated from finalized sales orders and invoices, excluding drafts and incomplete transactions.
- Reports can be filtered by product, product category, date ranges (day, month, year), and other relevant dimensions.
- Users can select which performance metrics to view, including but not limited to margin, quantity invoiced, untaxed total, and sales volume.
- Calculations of metrics such as margin are based on consistent pricing and cost data as defined in the product and invoice records.
- Currency conversions for sales involving multiple currencies are applied using the applicable exchange rates for the selected reporting period.
- The reporting interface provides multiple viewing options such as pivot tables, charts, and tabular data.
- Users can compare data across different periods (e.g., month-over-month, year-over-year) to identify trends and changes in sales performance.
- Reports can be exported directly into spreadsheets, maintaining applied filters and selected measures for offline analysis.
- The reporting data refresh frequency aligns with the transactional data updates, ensuring reports reflect the most recent finalized sales activity.
- Performance reporting excludes canceled, returned, or refunded transactions unless otherwise specified.
- Data integrity and accuracy are maintained by synchronizing sales, inventory, and accounting data within the Odoo system.
- Custom measures or KPIs can be added if configured by the system administrator, extending the standard set of performance indicators.
Screenshot