Odoo Inventory
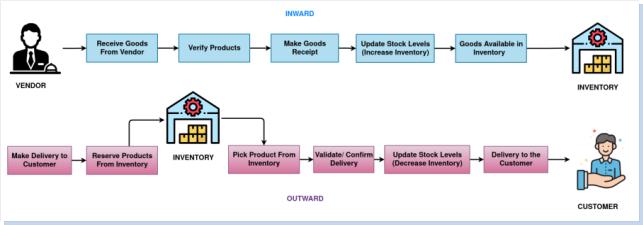
Inventory management is a critical process that involves tracking, organizing, and controlling a company’s stock of goods. It ensures that the right products are available at the right time to meet customer demand while minimizing excess inventory and associated costs. Key features often include real-time stock tracking, automated replenishment, multi-warehouse management, barcode scanning, and comprehensive reporting. Effective inventory management improves supply chain efficiency, reduces stockouts and overstock situations, and enhances overall operational productivity by providing clear visibility into stock levels and movements.
Odoo Inventory Key Features
- Track product quantities and movements live across warehouses and locations.
- Manage multiple warehouses and stock locations efficiently.
- Use barcode scanners for faster receiving, picking, packing, and shipping.
- Manage product variations (size, color, etc.) and track batches or serial numbers for traceability.
- Set minimum stock levels to automatically trigger purchase orders or manufacturing.
- Handle products sold or purchased in different units (e.g., pieces, boxes, kilograms).
- Ship directly from suppliers to customers without storing inventory; transfer products quickly without warehousing.
- Use batch, wave, or cluster picking to optimize warehouse workflows.
- Support FIFO, LIFO, average costing, and landed costs for accurate inventory valuation.
- Connect with major carriers (UPS, FedEx, DHL, USPS, etc.) for real-time rates, labels, and tracking.
- Perform quality checks and inspections with customized quality control workflows.
- Track product origins and expiry dates to maintain compliance, especially for perishable goods.
- Get detailed reports on stock levels, movements, forecasting, and warehouse performance.
- Manage stock transfers between different companies.
WorkFlow
Inventory Master Management
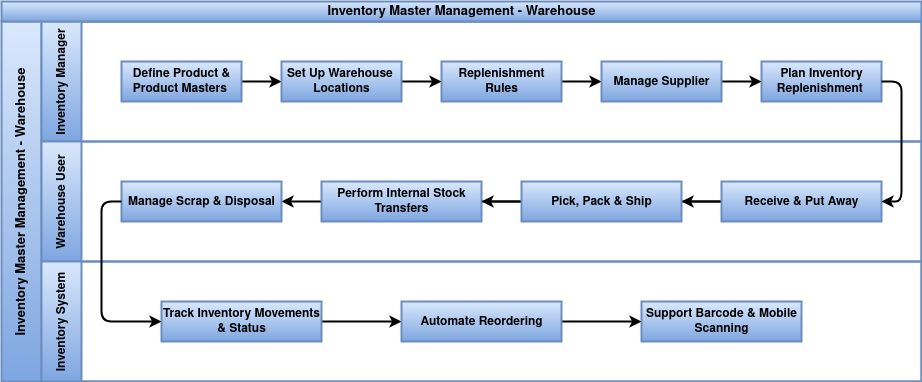
The Inventory Master Process is about accurately managing product and stock information like quantities, locations, and reorder levels. This helps prevent stock problems, ensures smooth warehouse operations, and supports timely purchasing and sales.
- Warehouse
- Locations
- Routes
- Putaway Rules
- Product Categories
- Attributes
- Unit of Measure
- Delivery Methods
- Package Types
- Products
- Product Variant
- Lot / Serial Number
- Package
Reporting
Odoo Inventory Reporting provides a comprehensive suite of reports to monitor and manage stock levels, product movements, warehouse operations, and inventory valuation. These reports support decision-making across warehouse, logistics, and accounting functions through real-time, filterable, and analytical data.
- Stock
- Locations
- Moves History
- Moves Analysis
- Valuation
Inventory Operation
Inventory handles the complete stock lifecycle, from procurement to delivery, including internal logistics and cost adjustments. It supports multiple warehouses and integrates tightly with sales, purchase, manufacturing, and accounting for smooth operations.
- Receipts
- Returns
- Deliveries
- Internal
- Manufacturing
- Drop ships
- Batch Transfers
- Physical Inventory
- Scrap
- Landed Costs
Inventory Master Management
Warehouse
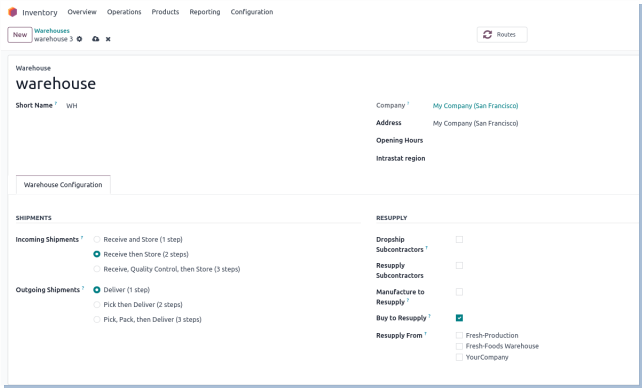
A warehouse is a storage location where goods are kept before they are sold or used. In inventory management, it helps track product quantities, movements, and storage locations. Proper warehouse setup ensures efficient stock handling, faster deliveries, and accurate inventory records.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Each warehouse must have a unique identifier (like WH01) to avoid confusion in inventory operations.
- In multi-company setups, a warehouse can belong to only one company. No sharing between companies.
- When a warehouse is created, Odoo automatically creates default locations like Stock, Input, Output, and Scrap.
- You need to set routes (like Buy, Manufacture, Dropship) to define how products move through the warehouse.
- Only users with the correct inventory or admin permissions can create or manage warehouses.
- Warehouses must be linked to delivery orders and receipts to handle incoming and outgoing stock.
- Moving products between warehouses must be done using internal transfers in Odoo.
- If your company uses automatic inventory valuation, you must set up correct accounting rules for each warehouse.
- Use consistent names and codes for clarity, especially in companies with multiple warehouses.
Screenshot
Locations
This document outlines the business rules for creating and managing Inventory Location Masters in Odoo to ensure accurate tracking, efficient warehouse operations, and system consistency.
Process Flow
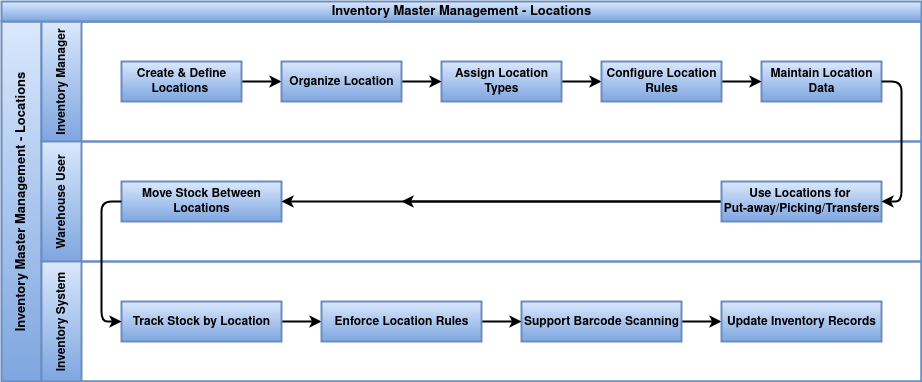
Business Rules
- Locations must have a defined type (internal, vendor, customer, production, inventory loss, or view).
- Location names must be unique within their parent location.
- Locations can be nested only in a way that avoids cyclic references (a location cannot be its own ancestor or descendant).
- Each location belongs to one warehouse or is a child of a warehouse location.
- Only stockable locations can hold inventory and record stock moves.
- Movement of products respects location usage rules (e.g., stock cannot move directly from vendor to customer locations).
- Default warehouse locations (input, stock, output, scrap) must not be deleted or renamed.
- Users require appropriate inventory permissions to create or modify locations.
- Locations must not be assigned as children to themselves or their descendants.
- Location setup must align with routing and putaway rules for correct automated stock flows.
- Location creation should prevent duplication or conflicting names within the same parent.
- Stock valuation and accounting processes depend on correct location usage settings.
Screenshot
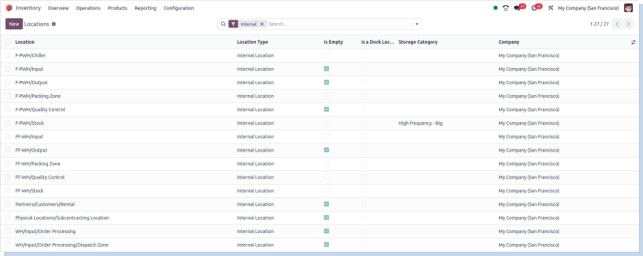
Routes
Odoo Inventory Routes define automated workflows that control how products move from suppliers to customers or within warehouses. They determine whether products are purchased, manufactured, stored, or shipped directly, helping streamline inventory management and order fulfillment. Routes can be set globally or per warehouse and support strategies like Make To Order, Drop Shipping, and Cross-Docking.
Process Flow
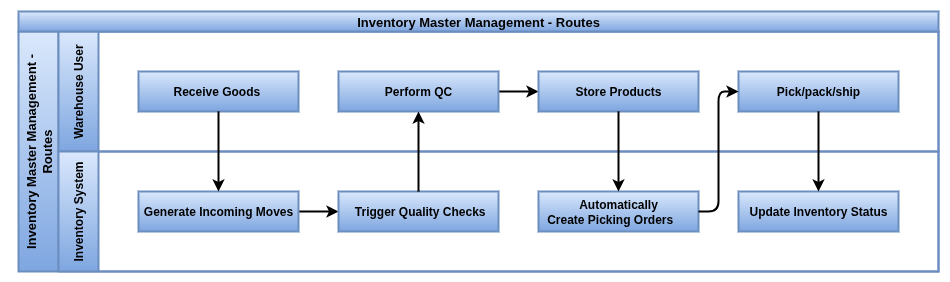
Business Rules
- Routes contain rules with conditions based on product, location, and procurement methods, which determine whether to pull from stock, manufacture, or buy.
- When a sales or purchase order is confirmed, Odoo checks the assigned routes to decide the flow of stock moves
- Pull rules trigger stock movement requests to source locations (e.g., suppliers or other warehouses).
- Push rules automate internal transfers within warehouses, such as moving products from receiving docks to storage.
- Make To Order routes delay procurement until sales confirmation, ensuring stock is only ordered or produced as needed.
- Drop Shipping routes create purchase orders that ship products directly from suppliers to customers without warehousing.
- Cross-Docking routes enable products to move immediately from receiving to shipping locations, minimizing storage time.
- Odoo integrates these routes with procurement and fulfillment workflows, automatically generating required orders and stock moves, reducing manual effort and errors.
Screenshot
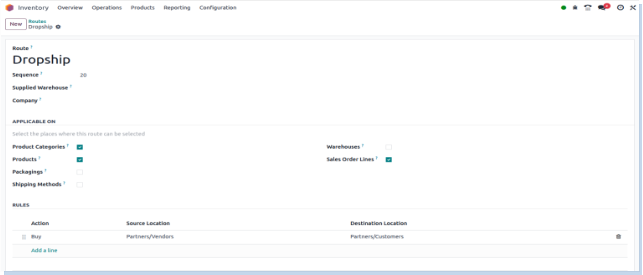
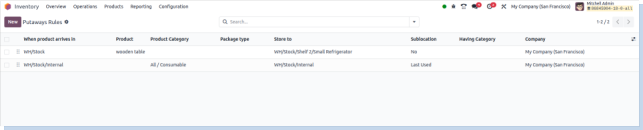
Putaway Rules
Overview
Putaway Rules in Odoo define how incoming products are automatically assigned to specific storage locations within a warehouse. They optimize space utilization and improve warehouse organization by guiding where products should be stored based on conditions like product type, category, or weight.
Process Flow
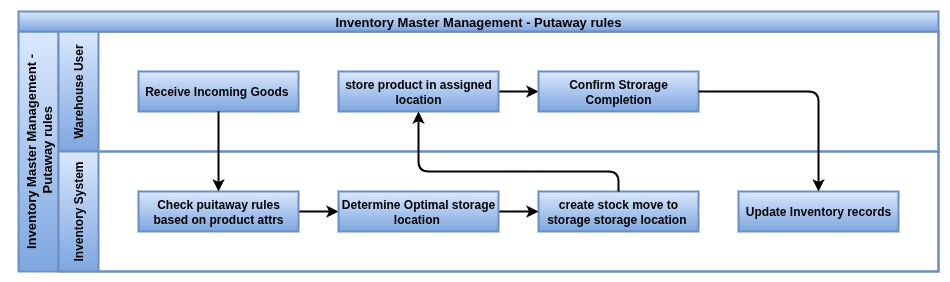
Business Rules
- When products arrive in the warehouse, Odoo checks putaway rules to decide the best storage location.
- Rules can be based on product attributes such as category, weight, volume, or serial number.
- Putaway rules prioritize locations with enough capacity and suitability for the product.
- If multiple rules apply, Odoo follows the order of priority set on the rules.
- This automation reduces manual sorting and speeds up inbound processing.
- Putaway rules integrate with routes and picking operations to ensure smooth stock flow.
Screenshot
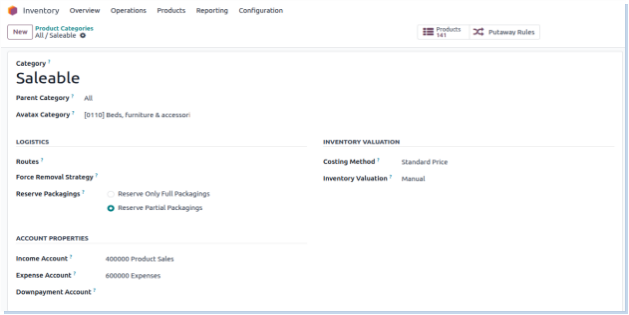
Product Categories
Product Categories group similar products to simplify inventory, purchasing, pricing, and accounting management. They allow applying common rules and settings across all products in a category, improving efficiency and consistency in operations.
Process Flow
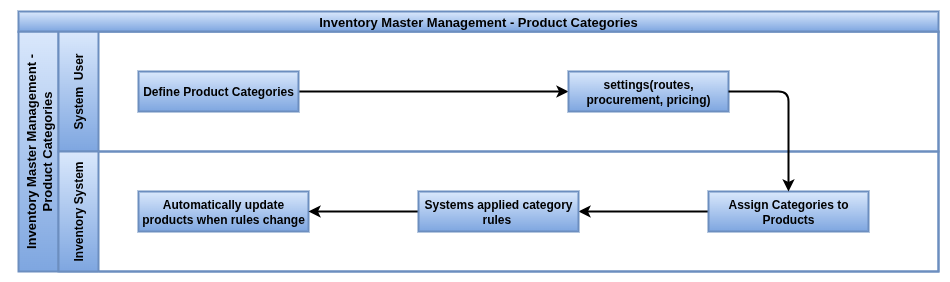
Business Rules
- Every product must belong to exactly one product category.
- Categories can be hierarchical, supporting parent-child relationships to organize products from broad to specific groups.
- Routes such as Make To Order or Drop Shipping can be assigned at the category level and will automatically apply to all products in that category.
- Procurement and replenishment rules set on categories dictate how products are purchased or manufactured.
- Accounting settings like expense accounts and valuation methods can be configured per category, ensuring accurate financial tracking.
- Product categories are used in reporting and filtering, enabling targeted stock analysis and decision making.
- Updating rules or settings at the category level cascades changes to all associated products, reducing manual updates.
Screenshot
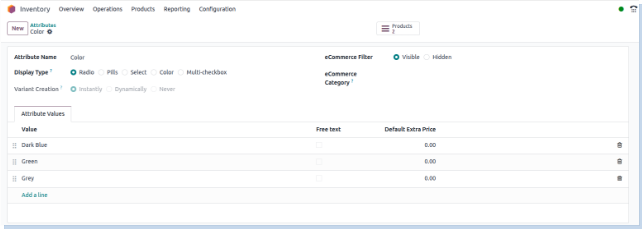
Attributes
Overview
Product attributes allow you to define key characteristics such as brand, color, size, material, or capacity for product templates. These attributes can be used to automatically generate product variants, influence pricing, and enhance product filtering in eCommerce. Each attribute includes a set of values and configuration options that determine how it appears in the backend, sales interfaces, inventory operations, and online store. Attributes not only help manage variants more effectively but also improve the customer experience through structured product catalogs and intelligent search filters.
Process Flow
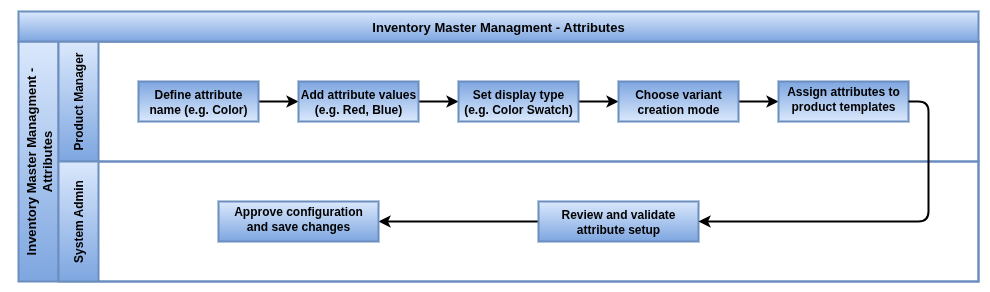
Business Rules
- Each product attribute must have a unique name and at least one associated value.
- Attributes can be configured to create product variants either instantly, dynamically, or never, depending on operational needs.
- Only attributes with variant creation enabled will generate product variants that affect inventory and stock tracking.
- The display type (radio, dropdown, pills, color, etc.) controls how the attribute is shown in forms and on the website.
- Attributes set to “Never” for variant creation are used purely for informational or filtering purposes and do not affect inventory.
- Attribute values can include extra pricing to adjust the final sale price when selected.
- Attributes used in eCommerce should have eCommerce Filter set to “Visible” if they are to appear as product filters in the storefront.
- Product templates using multiple attributes will automatically generate combinations (variants) based on the values and variant creation setting.
- Each variant can have independent settings such as stock level, barcode, and sales price.
- All attribute configurations must be maintained by users with appropriate access rights to ensure product consistency and data integrity.
Screenshot
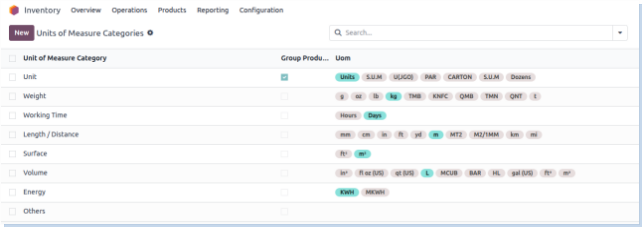
Units of Measure
Overview
Units of Measure (UoM) in Odoo define how product quantities are managed, sold, purchased, and stored. They enable flexibility in handling products across different operations by supporting conversions between units (e.g., units, boxes, kg, liters).
Process Flow
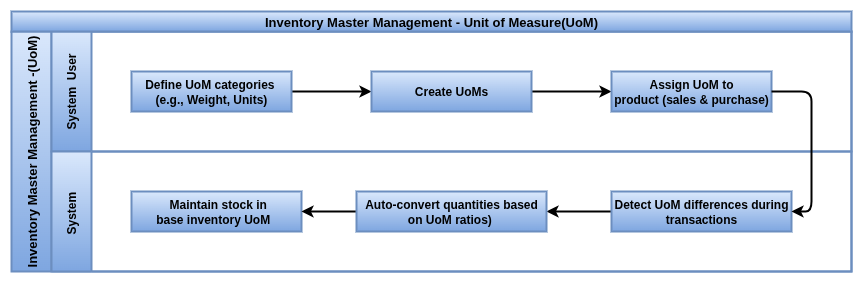
Business Rules
- Every product is assigned a default Unit of Measure (UoM) for inventory operations.
- Products can have a different purchase UoM, which Odoo automatically converts based on the UoM category.
- Units of Measure are grouped into categories (e.g., Weight, Volume, Length) — conversion is only allowed within the same category.
- UoM conversions are defined with precision and ratios (e.g., 1 box = 10 units).
- All transactions (purchases, sales, transfers) respect the defined UoM and apply automatic conversion if needed.
- Accurate UoM setup ensures correct inventory valuation, procurement quantities, and reporting.
- UoM rounding precision helps prevent quantity mismatches during automated processes.
- UoM category cannot be changed once used in transactions to maintain data integrity.
Screenshot
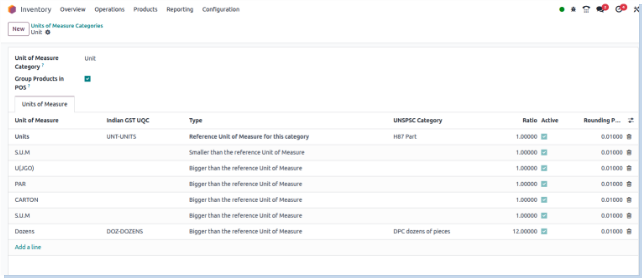
Delivery Methods
Overview
Delivery Methods in Odoo allow businesses to manage shipping operations by integrating with carriers (e.g., DHL, FedEx) or configuring manual delivery options. They help automate delivery cost calculation, track shipments, and select the most efficient shipping option during sales or inventory processes.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Delivery methods can be manually configured or integrated with third-party shipping carriers.
- Each delivery method can have pricing rules based on fixed price, weight, volume, or destination.
- Delivery methods can be assigned to sales orders, websites, or directly applied in shipping operations.
- Odoo can compute delivery costs automatically based on product quantities, weight, and chosen delivery method.
- Integrated carriers allow real-time rate calculation, label generation, and tracking links.
- A default delivery method can be assigned per customer or sales channel.
- Delivery charges can be added to the sales order/invoice as separate lines.
- Users can manually override or recalculate shipping rates before confirming the order.
- Only one delivery method is used per order or shipment operation.
Screenshot
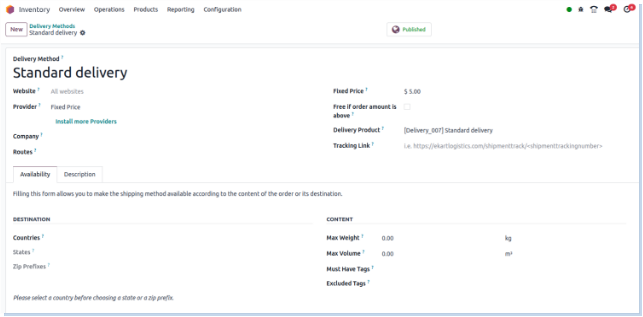
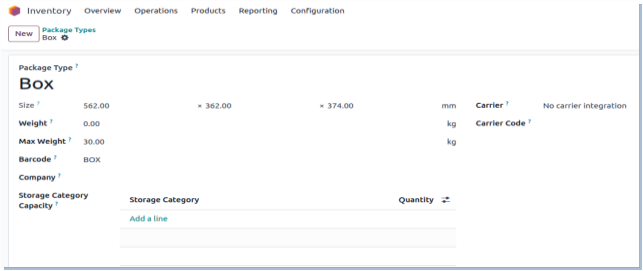
Package Types
Overview
Package Types in Odoo define how products are grouped and packed for storage and shipment. They improve handling efficiency, enable accurate shipping calculations, and support better inventory tracking.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Package types classify packing units like boaxes, pallets, or crates with specific size and weight attributes.
- Each package type has dimensions (length, width, height) and maximum weight to ensure compliance with shipping carrier requirements.
- Package types can be assigned automatically using putaway or packing rules or manually by warehouse staff.
- Packages can contain multiple products or multiple units of the same product.
- When shipping, package types influence shipping costs, label printing, and carrier selection.
- Packages are tracked individually during inventory moves and deliveries to provide traceability.
- If products require special handling, specific package types can be mandated.
- Package types support nested packing (e.g., boxes inside pallets).
- Changing package types after shipping is restricted to maintain accuracy.
Screenshot
Inventory Products
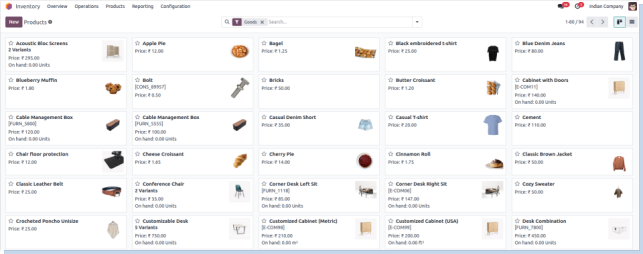
Products
Overview
Odoo Inventory is a modern, scalable solution designed to optimize warehouse management and stock control. With advanced features like multi-warehouse support, real-time product tracking, automated replenishment, and deep integration with Odoo’s sales, purchase, and manufacturing apps, it empowers businesses to maintain accurate inventory, reduce stockouts, and improve fulfillment speed and accuracy.
Process Flow
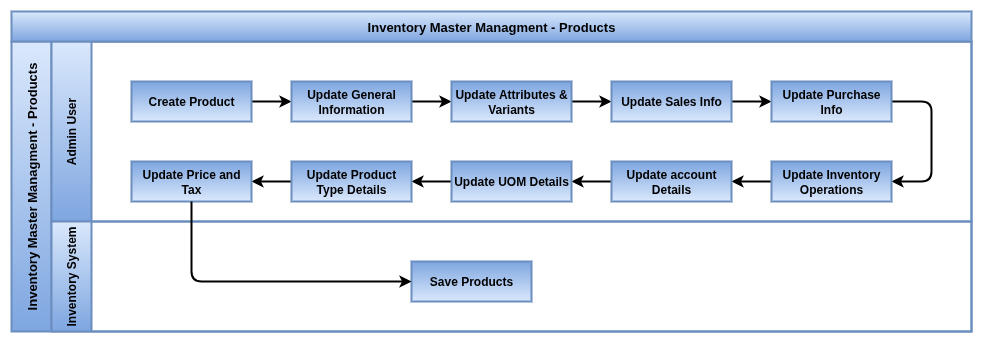
Business Rules
- Only products marked as Stockable are tracked with real-time quantity updates in the inventory system; consumables and services are managed differently.
- Lot and serial number tracking is fully supported, allowing precise traceability from receipt to delivery, essential for compliance and quality control.
- Warehouses are divided into hierarchical locations (aisles, shelves, bins), enabling granular stock management and efficient picking strategies.
- Every stock movement (receipt, delivery, internal transfer) is recorded as a stock move; stock quantities are updated immediately upon validation.
- Replenishment rules can be configured using minimum and maximum stock levels per product and warehouse, automatically triggering purchase orders or manufacturing orders when stock is low.
- Procurement can be set to Make to Order or Buy, allowing flexible sourcing strategies aligned with demand and supply conditions.
- Odoo supports automated barcode scanning and IoT device integration to streamline warehouse operations and reduce manual errors.
- Regular inventory adjustments and cycle counts ensure stock accuracy, with variance tracking and detailed audit logs.
- Role-based access rights and approval workflows safeguard inventory integrity, restricting sensitive operations to authorized personnel.
- Complete audit trails provide full visibility into stock movements and user actions for regulatory compliance and operational transparency.
Screenshot
Product Variants
Overview
Manage products with multiple variants efficiently. Whether it’s different sizes, colors, or other attributes, product variants help you offer a wide range of options without creating separate products for each variation. This keeps your inventory organized and simplifies stock tracking and sales processes.
Process Flow
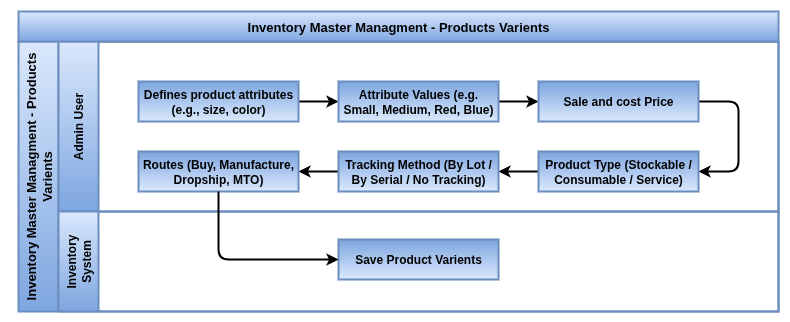
Business rules
- Products can have multiple attributes (e.g., size, color, material), and each unique combination forms a variant.
- Variants are treated as individual stockable items with their own SKU, barcode, price, and inventory levels.
- You can configure attribute values to affect cost, price, and availability at the variant level.
- Variants can be managed across multiple warehouses and locations with accurate stock tracking.
- The system supports variant-specific barcodes and serial numbers, enabling precise identification and traceability.
- Sales, purchase, and manufacturing processes seamlessly handle variants, ensuring correct variant selection at every step.
- Variants simplify catalog management by consolidating all options under a single product template, reducing duplication.
- Variant rules and filters can be used in reporting and replenishment, enabling granular inventory control.
Screenshot
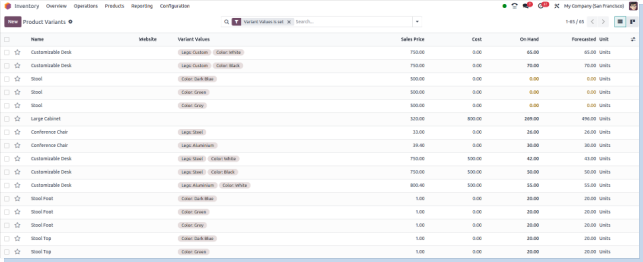
Lots and Serial Numbers
Overview
Odoo offers robust lot and serial number management to ensure complete traceability and control over your inventory. Whether you need batch tracking for quality control, expiry dates, or unique serial tracking for warranty and service, Odoo lets you handle all these requirements seamlessly.
Process Flow
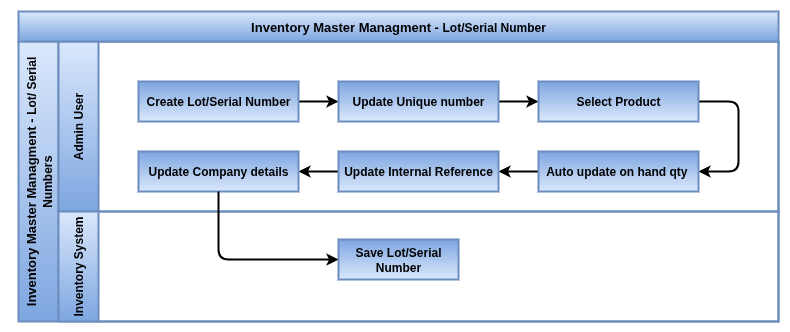
Business Rules
- Lot Numbers group products in batches, allowing you to track production runs, expiration dates, and quality checks.
- Serial Numbers provide unique identifiers for individual items, essential for warranty management, repairs, and after-sales support.
- Lot and serial number tracking can be enabled per product, depending on the business need.
- Every stock move (receipt, internal transfer, delivery) records the lot or serial numbers involved, ensuring precise traceability.
- Integration with barcode scanners supports quick scanning of lot and serial numbers during warehouse operations.
- You can configure lot expiration dates, and Odoo can automatically alert you to products nearing expiry to reduce waste.
- Traceability reports allow tracking the history of a lot or serial number from supplier to customer, including manufacturing, storage, and sales data.
- Serial and lot numbers can be used in quality control workflows, enabling inspections and blocking defective batches or items.
- User access controls restrict who can assign or modify lot and serial numbers to maintain data integrity.
Screenshot
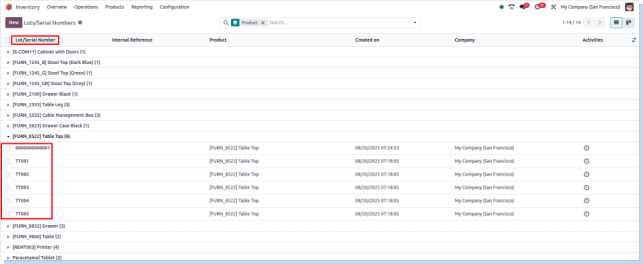
Packages
Overview
Odoo allows you to manage products grouped into packages, streamlining warehouse handling and shipping processes. Packages help organize multiple products into single units for easier storage, picking, and delivery, improving overall warehouse efficiency.
Process Flow
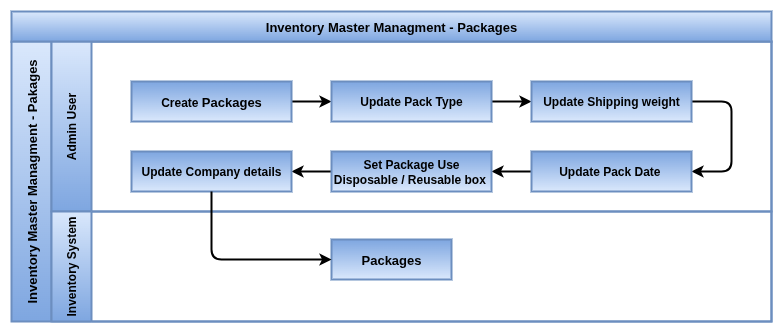
Business Rules
- Packages can contain one or more products, each with specific quantities, allowing bulk handling of grouped items.
- Packaging can be customized per warehouse, shipment, or customer requirements.
- Each package is assigned a unique identifier (package ID or barcode) for tracking throughout the warehouse and delivery cycle.
- During picking and shipping, packages can be scanned as single units, speeding up operations and reducing errors.
- Packages can be nested — for example, pallets containing multiple boxes — to match complex logistics workflows.
- Inventory adjustments and stock moves track packages alongside individual products to maintain accurate inventory levels.
- Packages support integration with delivery carriers and shipping labels, enabling seamless logistics management.
- User roles and permissions control packaging operations, ensuring correct handling and compliance.
Screenshot
Inventory Operations
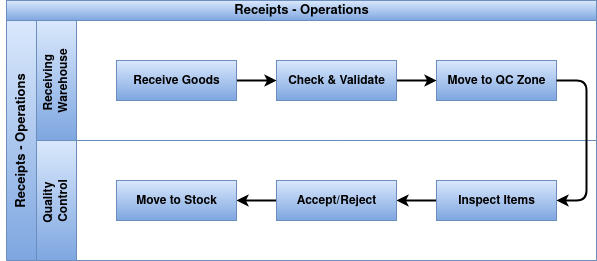
Receipts
Inventory Receipts in Odoo refer to the process of receiving products into the warehouse from suppliers or other sources. This operation involves creating a Receipt Order that records the incoming goods, updating stock levels, and verifying the received quantities.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Receipts are automatically created when a Purchase Order is confirmed.
- Manual receipts can be created for stock transfers without Purchase Orders.
- All incoming receipts must be validated within 24 hours of goods arrival.
- If receipt validation is delayed beyond 24 hours, notify the warehouse manager.
- Quantities received must match Purchase Order quantities.
- Partial receipts are allowed and must be flagged for review if quantities differ.
- Goods flagged for quality control require inspection before receipt validation.
- Receipts cannot be validated without quality approval for flagged products.
- Serial or lot numbers must be recorded for tracked products before validating receipts.
- Only authorized warehouse staff can create and validate receipts.
- Manager approval is required for receipts exceeding a set value threshold.
- Backorders automatically generate partial receipts for pending items.
- Receipts must specify the correct destination stock location, defaulting based on product or PO settings.
Screenshot
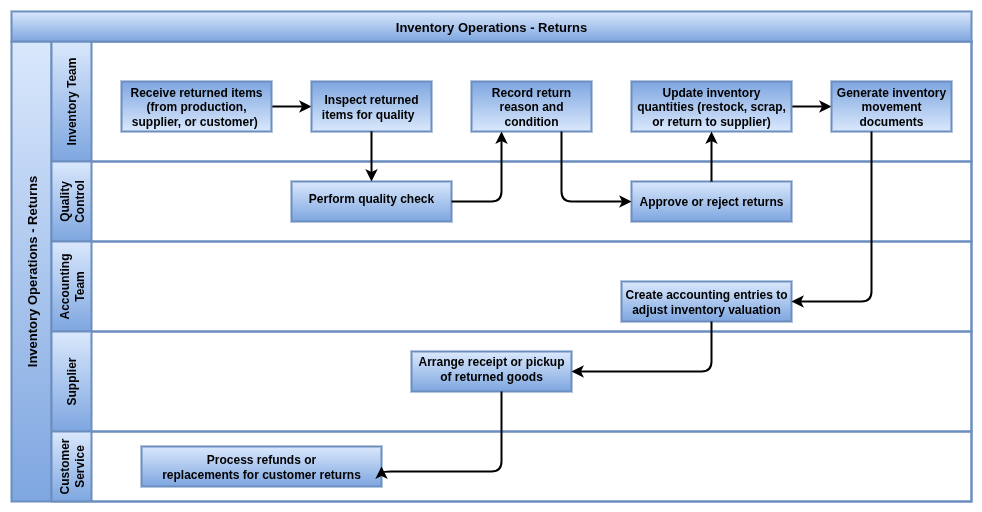
Returns
Overview
The Return Operation in Odoo Manufacturing manages the process of returning finished goods or raw materials back to inventory or suppliers. This operation handles quality issues, defects, excess production, or customer returns. It ensures accurate inventory updates, proper accounting adjustments, and traceability of returned items for quality control and audit purposes. Returns can trigger rework, replacement manufacturing, or credit notes depending on the situation.
Process flow
Business Rules
- Returns must be linked to an original Manufacturing Order (MO), Purchase Order (PO), or Sales Order (SO) to maintain traceability.
- Returned finished goods or raw materials must be inspected and quality checked before acceptance.
- Returns can trigger rework orders or scrap processes based on quality inspection results.
- Inventory quantities are updated immediately upon processing the return to reflect accurate stock levels.
- Accounting entries are automatically generated to adjust inventory valuation and financial records.
- Only authorized users can initiate, approve, and validate return operations.
- Returned raw materials can be restocked if approved; otherwise, they must be scrapped or returned to suppliers.
- Customer returns may initiate refund or replacement workflows linked to Sales Orders.
- All return operations are logged for audit trail and reporting purposes.
- Return workflows integrate with Quality Control and Maintenance modules to handle defective products and equipment issues.
- Partial returns are supported, allowing flexibility in handling batch or lot-based products.
Screenshot
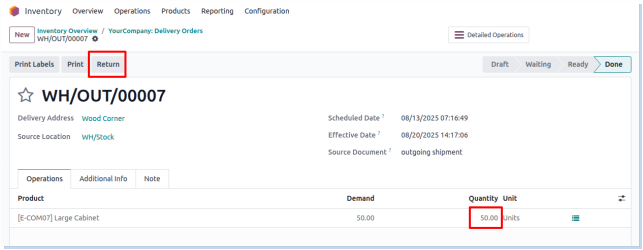
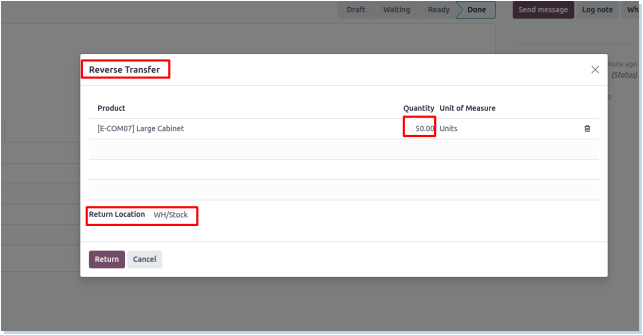
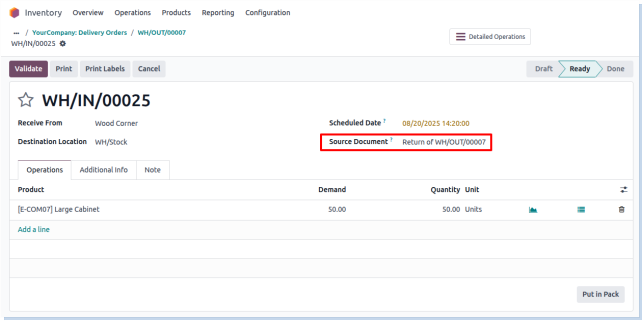
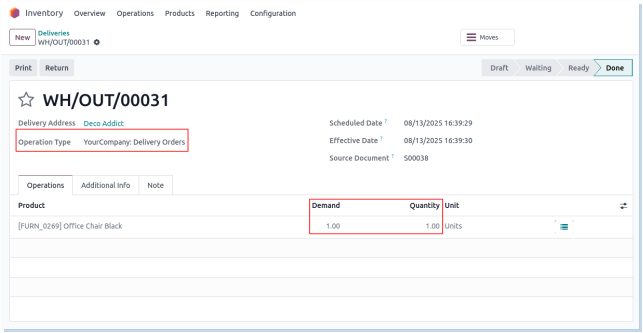
Deliveries
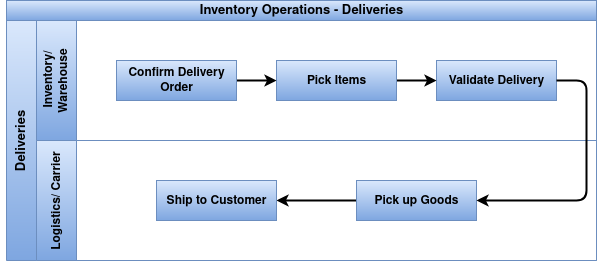
Overview
Odoo Delivery Operations manage the process of shipping products from warehouses to customers. This includes preparing delivery orders, validating shipments, managing carriers and shipping methods, and tracking deliveries to ensure timely fulfillment and customer satisfaction.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Each sales order generates a delivery order (picking) to prepare products for shipment.
- Delivery orders are linked to specific warehouses and stock locations.
- Delivery operations respect product availability and reservation rules before shipment.
- Multiple delivery orders can be grouped or split based on carrier, destination, or product type.
- Carriers and delivery methods (e.g., FedEx, UPS, Local Courier) are configured with costs and tracking options.
- Delivery orders must be validated (done status) to confirm shipment and update inventory levels.
- Tracking numbers and delivery statuses are recorded and shared with customers when available.
- Partial deliveries are allowed if not all items are ready to ship at once.
- Returns and exchanges are processed through reverse delivery orders with proper stock adjustments.
- Delivery schedules can be planned and optimized for route and cost efficiency.
- Integration with invoicing and sales ensures shipment triggers billing and revenue recognition.
- Real-time stock updates occur when delivery orders are validated.
- Alerts and notifications can be configured for shipment delays or exceptions.
Screenshot
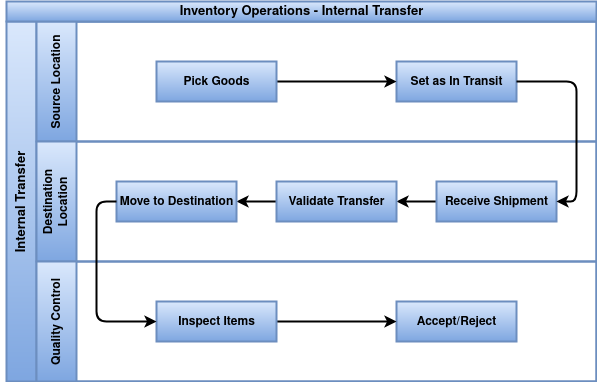
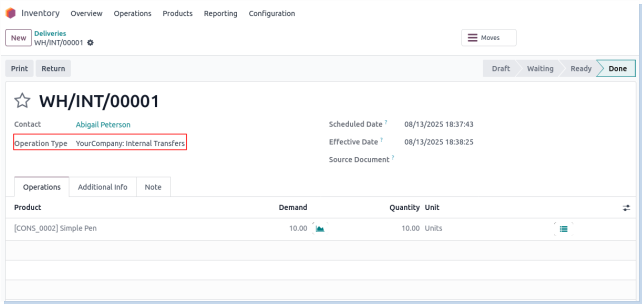
Internal Transfer
Internal refer to the movement of stock between different locations or warehouses within the same company. This process helps balance inventory, fulfill internal demands, or relocate products for operational efficiency.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Internal are initiated by creating a transfer order between source and destination locations.
- Only authorized personnel can create, validate, and complete internal transfers.
- Transfer quantities must match the requested amounts unless partial transfers are approved.
- Transfers must be validated within a set timeframe (e.g., 24-48 hours) after initiation.
- Stock availability in the source location must be confirmed before transfer validation.
- Serial or lot numbers must be recorded and tracked during transfer for applicable products.
- Transfers should specify correct source and destination locations clearly.
- Any discrepancies or damages during transfer must be reported and addressed immediately.
- Internal transfers do not require customer approval but may require managerial review for high-value items.
- Stock levels in both locations are updated only after transfer validation is complete.
Screenshot
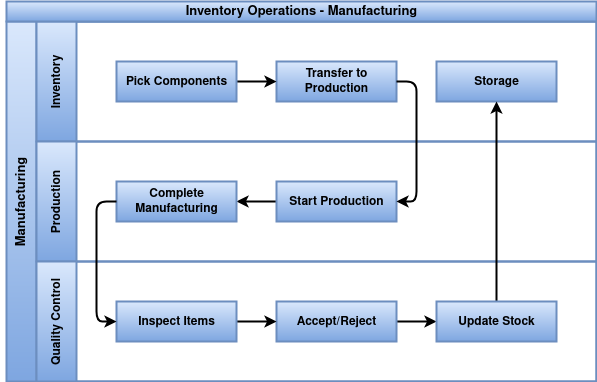
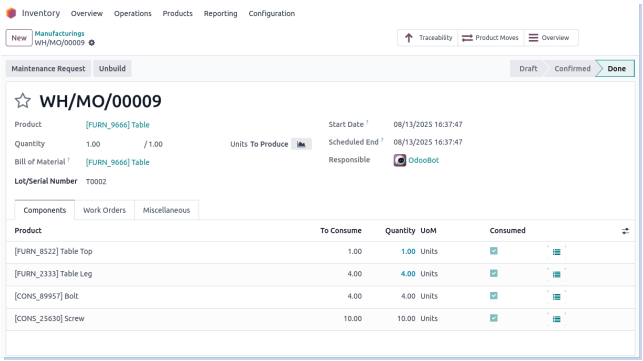
Manufacturing
Manufacturing involves converting raw materials into finished products through a production process. It requires planning, tracking material consumption, and updating inventory levels of both raw materials and finished goods.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Manufacturing orders (MOs) are created based on demand or production planning.
- Only authorized production staff can create, start, and validate manufacturing orders.
- Raw materials required for production must be available and reserved before starting the MO.
- Consumption of raw materials is recorded and deducted from inventory when production starts or completes.
- Finished products are added to inventory only after the manufacturing order is validated.
- Quality checks must be performed on finished goods before completing the manufacturing order.
- Partial manufacturing is allowed; partially finished goods must be tracked separately.
- Serial or lot numbers must be assigned to finished products if applicable.
- Any scrap or waste generated must be recorded and deducted from inventory.
- Changes in the bill of materials (BOM) require approval before use in manufacturing orders.
Screenshot
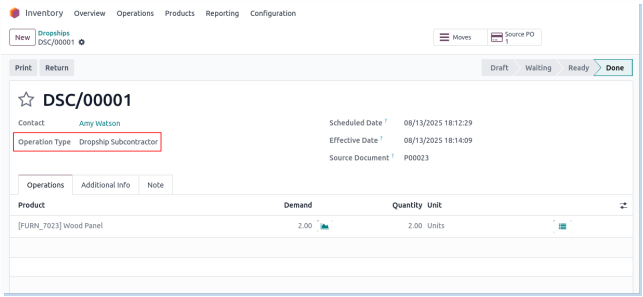
Drop shipping
Drop shipping is a fulfillment method where products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer, bypassing the company’s warehouse. This eliminates the need to hold inventory but requires careful coordination between purchase, sales, and supplier shipping.
Business Rules
- Dropship orders are created automatically from confirmed sales orders flagged for dropshipping.
- Purchase Orders are generated directly to the supplier for the items to be shipped.
- No physical inventory is received or stored by the company for dropshipped products.
- Only authorized staff can create and manage dropship purchase orders.
- Supplier must confirm shipment and provide tracking information before sales order delivery validation.
- Customer delivery address is sent directly to the supplier and must be verified for accuracy.
- Communication with the supplier should be maintained to track shipment status.
- Payment terms and invoicing for dropship items must be clearly defined and followed.
- Dropship shipments must be validated before marking the sales order as delivered.
- Any issues with supplier shipment delays or errors must be escalated immediately.
Screenshot
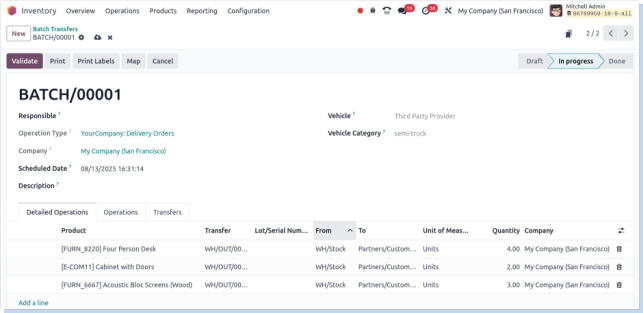
Batch Transfers
Overview
Batch transfers involve grouping multiple stock transfers (e.g., receipts, deliveries, or internal transfers) into a single operation to streamline processing. This is useful for managing high-volume movements efficiently and consistently.
Business Rules
- Batch transfers group multiple individual transfers of the same type (e.g., all deliveries or all receipts).
- Only authorized users can create, assign, and validate batch transfers.
- All transfers in a batch must be in the same state (e.g., ready or waiting) before batching.
- Transfers must share the same operation type (e.g., delivery or internal) to be included in a batch.
- Each batch must have a responsible user or operator assigned.
- Validation of a batch validates all included transfers simultaneously.
- Any failed or incomplete transfer within a batch must be reviewed separately and reprocessed.
- Batches must be processed within the scheduled time frame to avoid shipment or transfer delays.
- Audit trails must be maintained for all batch operations for traceability.
- Barcode scanning (if enabled) must verify each line item during batch picking or transfer.
Screenshot
Physical Inventory
Overview
Physical inventory is the process of counting actual stock in a warehouse to verify and adjust system-recorded quantities for accuracy.
Process Flow
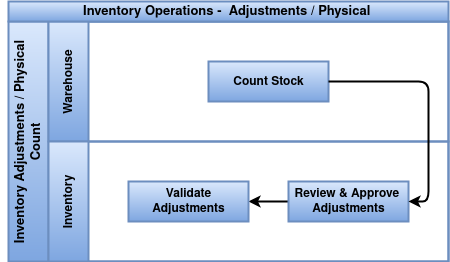
Business Rules
- Physical inventory must be scheduled periodically (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually).
- Only authorized users can create and validate inventory adjustments.
- All counting must be done without moving stock during the process (freeze stock if necessary).
- Discrepancies between counted and system quantities must be reviewed and justified.
- Adjustments must be approved before being applied to inventory levels.
- Physical inventory records must be stored for auditing and traceability.
- Use of barcode scanning is recommended to increase counting accuracy.
Screenshot
Scrap
Overview
Scrap refers to damaged, expired, or unusable stock that needs to be removed from available inventory.
Process Flow
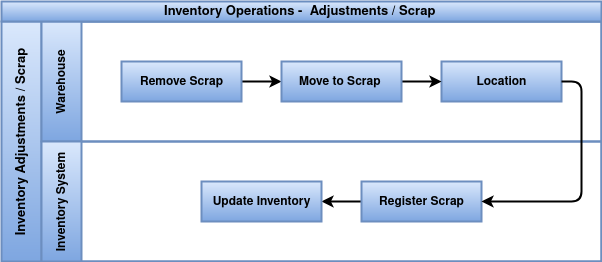
Business Rules
- Scrap movements must be recorded using a dedicated scrap location.
- Only authorized staff can declare stock as scrap.
- The reason for scrapping must be documented (e.g., damaged, expired, production waste).
- Scrap items must be removed from available stock immediately after validation.
- Manager approval may be required for high-value or frequent scrap events.
- Scrap records must be maintained for reporting and loss analysis.
- Scrap from manufacturing must be linked to the corresponding production order.
Screenshot
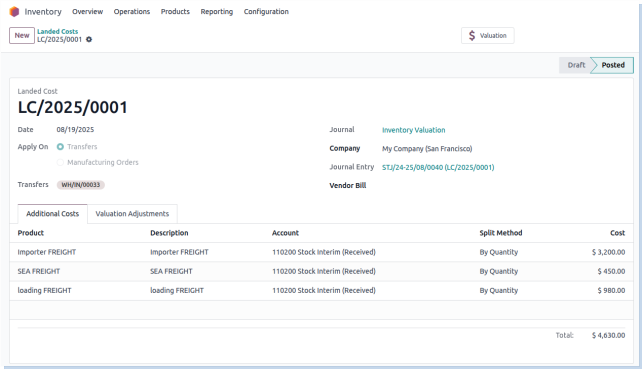
Landed Costs
Overview
Landed costs are the additional expenses incurred to bring products to a warehouse, such as shipping, customs, and insurance. These costs are distributed across product values.
Process Flow
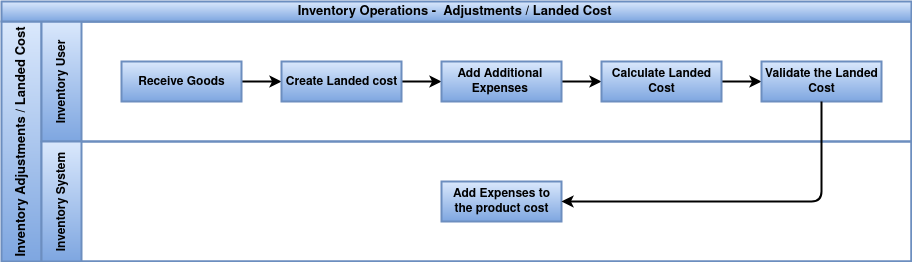
Business Rules
- Landed costs must be linked to incoming shipments or receipts.
- Only authorized users can create and allocate landed cost documents.
- Landed costs can be split by quantity, weight, volume, or manually across products.
- Landed cost entries must be validated before impacting product valuation.
- Costs must be included in product valuation for real or average cost methods.
- Proper accounts must be configured for landed cost adjustments.
- All supporting documents (e.g., invoices, freight bills) must be attached to the landed cost record.
Screenshot
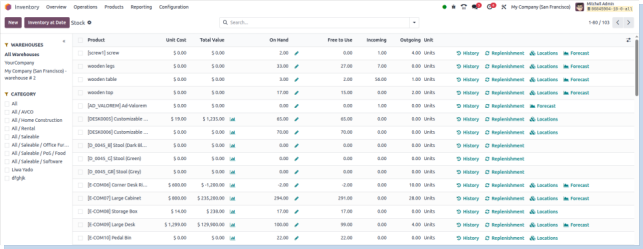
Reporting
Stock
Overview
Displays product stock levels across all warehouses and locations in real time, helping users monitor inventory availability, shortages, and movement status.
Business Rules
- Tracks actual product quantities: on-hand, incoming, outgoing, and forecasted.
- Filters enable segmentation by product, category, warehouse, location, and date.
- Real-time updates reflect completed transactions (e.g., receipts, deliveries).
- Supports stock audits and supply chain analysis.
- Helps detect negative stock levels or overstock situations.
- Enables export for use in planning or communication.
- Supports internal transfer validation by comparing expected vs actual stock
Screenshot
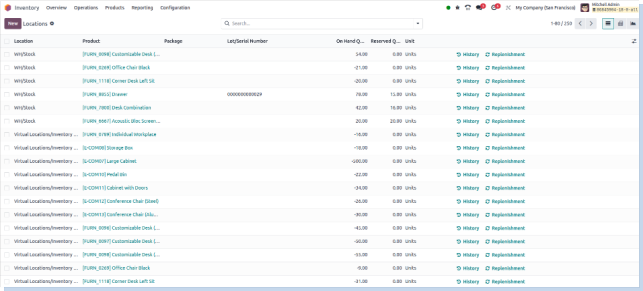
Locations
Overview
Provides visibility into the warehouse structure and the precise locations (e.g., zone, shelf, bin) where each product is stored.
Business Rules
- Represents storage hierarchy using parent-child location relationships.
- Reports show stock quantities grouped by location.
- Helps locate misplaced or unaccounted stock.
- Facilitates zone-based inventory planning and optimization.
- Enables location-based filtering for inventory adjustments and audits.
- Improves space utilization tracking.
- Assists in identifying which locations hold specific product categories.
Screenshot
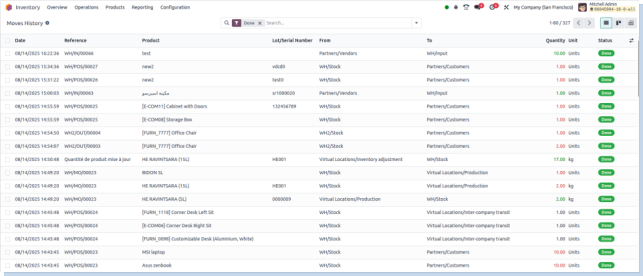
Moves History
Overview
Lists detailed records of all stock movements such as incoming shipments, internal transfers, deliveries, and returns.
Business Rules
- Logs every move with date, source, destination, user, and quantity.
- Move status is tracked (e.g., draft, waiting, done, cancelled).
- Filterable by product, date range, location, or partner.
- Helps identify discrepancies in movement and delays in processing.
- Enables backtracking to resolve stock mismatches.
- Provides audit trails for compliance and operational reviews.
- Supports performance evaluation of warehouse processes
Screenshot
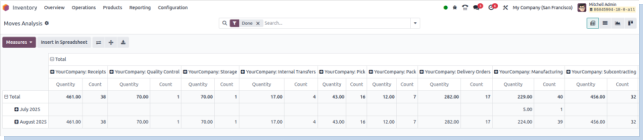
Moves Analysis
Overview
Aggregates and analyzes stock movements over time to reveal patterns in inventory flow and warehouse activity.
Business Rules
- Summarizes incoming and outgoing product volumes.
- Groups movements by operation type, product, location, or date range.
- Highlights trends in demand and supply behavior.
- Identifies high-velocity or dormant products.
- Useful for planning procurement and restocking.
- Supports forecasting based on historical movement data.
- Aids in workload balancing among warehouse teams.
Screenshot
Valuation
Overview
Odoo provides real-time stock valuation reports that track the value of raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods, and scrap. Reports use Standard, FIFO, or Average costing methods and offer detailed insights into production costs and inventory value. Full traceability, drill-down analysis, and secure access help manufacturers manage costs, ensure accuracy, and support financial reporting.
Business Rules
- Stock valuation reports reflect inventory value using the costing method configured in Odoo EE (Standard, FIFO, or Average Cost).
- Reports provide detailed breakdowns of raw materials consumed, work-in-progress (WIP) valuation, finished goods, and scrap costs.
- Valuation data is updated in real-time, leveraging Odoo EE’s advanced real-time inventory and accounting integration.
- Reports compare planned production costs against actual costs, highlighting variances for better cost control and efficiency analysis.
- All stock valuation entries are traceable to specific Manufacturing Orders (MOs) and Work Orders (WOs), supporting full audit trails.
- Historical valuation data is maintained and accessible to enable trend analysis, forecasting, and compliance reporting.
- Inventory transactions affecting valuation (material consumption, scrap, production completion) are automatically recorded and reflected in reports.
- Access controls restrict report visibility to authorized users, ensuring confidentiality and data integrity within Odoo EE’s robust security framework.
- Drill-down features allow detailed analysis by product, production batch, work center, or date range, enhancing decision-making capabilities.
- Adjustments or corrections to stock valuation require proper documentation and approval, maintaining accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Screenshot
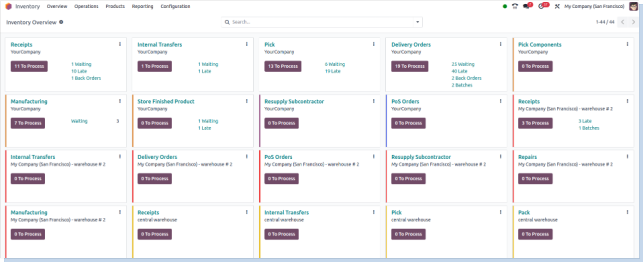
Inventory Dashboard
Overview
The Inventory Dashboard in Odoo delivers a comprehensive, real-time snapshot of your entire inventory operations. It consolidates data from multiple warehouses, product categories, and stock locations, providing visibility into stock levels, movements, and valuation. The dashboard supports proactive inventory management through automated alerts for low stock, reorder points, and aging products. Advanced reporting and graphical insights help optimize procurement, sales, and manufacturing decisions.
Key Features
- Unified, real-time inventory status across all warehouses and locations
- Detailed stock valuation using methods like FIFO, Average Cost, or Standard Price
- Automated low-stock alerts and reorder notifications to avoid stockouts
- Visual charts displaying stock levels, incoming shipments, and outgoing deliveries
- Product category performance summaries to identify best-sellers and slow movers
- Quick access to detailed stock movement reports and audit trails
- Filter and drill-down options by warehouse, product type, or date range
- Integration with purchase, sales, and manufacturing modules for seamless flow
Screenshot