Odoo Manufacturing
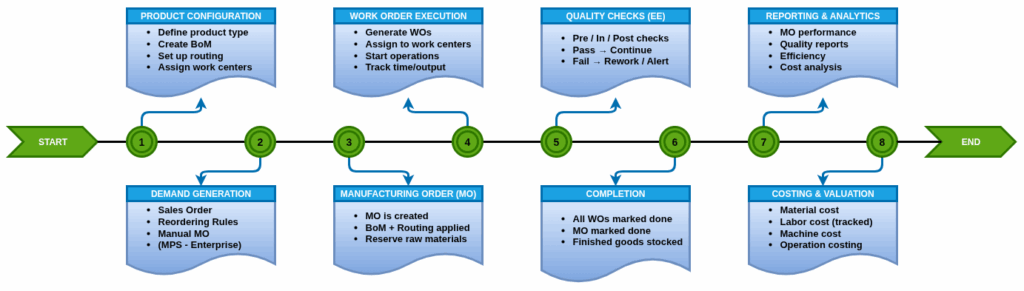
The Manufacturing module provides a comprehensive and fully integrated management system designed for modern manufacturing businesses. It enables users to efficiently plan, schedule, execute, and monitor production activities all within a single platform.
With features like Bill of Materials (BoM), Routing, Work Orders, Shop Floor Control, Quality Checks, and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), the system supports both discrete and process manufacturing operations. It integrates seamlessly with Inventory, Sales, Purchase, Maintenance, and Accounting modules to ensure smooth coordination across departments.
Advanced tools such as Master Production Scheduling (MPS), Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) monitoring, Work Order time tracking, and Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) enhance visibility and control over the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
Whether managing custom builds, repetitive production, or complex multi-level BoMs, this solution delivers the flexibility and automation needed to optimize productivity, reduce waste, and ensure product quality.
Work Flow
Business Rules
- A product must be configured with the “Manufacture” route to be included in the production process.
- A Bill of Materials (BoM) must exist for any product to be manufactured.
- Only one default BoM is allowed per product; additional BoMs can be created for variants or alternatives.
- Manufacturing Orders (MOs) cannot be confirmed without a valid BoM and required components.
- Work Orders (WOs) are automatically generated only if a routing is linked to the BoM.
- Work Orders must follow the defined operation sequence in the routing unless parallel operations are allowed.
- Work Orders cannot be started unless all required raw materials are available or manually forced.
- Materials are automatically reserved from stock when an MO is confirmed.
- If stock is unavailable, the system follows procurement rules to trigger purchases or transfers.
- Time tracking on Work Orders is required for accurate labor costing and performance analysis.
- Finished products are not added to inventory until the Manufacturing Order is marked as done.
- Material consumption can be strict (based on BoM) or flexible (actual consumption entered during production).
- Quality checks are enforced based on Quality Points defined for the product, operation, or BoM.
- Failed quality checks must trigger rework, rejection, or maintenance actions.
- Scrap must be recorded and tracked with reasons during any step of production.
- Routing steps must be completed in sequence unless explicitly configured for overlap.
- Machine or labor costs are calculated based on tracked time and work center rates.
- Journal entries for production costs are automatically generated if real-time valuation is enabled.
- Inventory movements must reflect actual component usage and finished product quantities.
- Production cannot proceed beyond current work orders if any prior step fails or is blocked.
- Maintenance requests must be created if a work center fails during execution.
- ECOs (Engineering Change Orders) must follow an approval process before BoMs or routing can be modified.
- Only users with appropriate permissions can edit, cancel, or validate Manufacturing Orders.
- MOs must be closed before reporting production costs or transferring products to stock.
- Costing must reflect actual material usage, labor time, and machine operation for each production run.
- Reordering rules trigger MOs only when product stock falls below the minimum quantity defined.
- The system must prevent duplicate MO creation unless manually overridden by authorized users.
- Production planning must consider work center capacity, availability, and shift schedules.
- All changes to MOs, BoMs, or routing must be logged for traceability and audit purposes.
- Reports must show planned vs. actual performance, cost variance, and quality statistics.
Manufacturing Master Management
- Products
- Product Variants
- Bills of Materials
- Lots/Serial Numbers
- Work Centers
- Operations
Manufacturing Operations Management
- Manufacturing Orders
- Work Orders
- Unbuild Orders
- Scrap
Manufacturing Planning Management
- Planning by Production
- Planning by Work center
- Master Production Schedule
Manufacturing Reporting
- Work Orders
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness
- Production Analysis
Manufacturing Dashboard
Overview
The Manufacturing Dashboard in Odoo provides a centralized and real-time overview of all manufacturing operations, enabling production managers and teams to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
Dashboard Visual Insights
- Work Orders Status – Track progress, delays, and completion of work orders.
- Manufacturing Orders (MOs) – View the current status of MOs: confirmed, planned, in progress, or completed.
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) – Monitor equipment performance and availability to optimize productivity.
- Inventory Levels – Stay updated on the availability of raw materials and finished goods.
- Production KPIs – Analyze key performance indicators like production lead time, scrap rates, and efficiency.
- Gantt and Calendar Views – Schedule and manage production timelines with ease using visual planning tools.
- Quality Alerts and Maintenance Activities – Get real-time updates on quality checks and machine maintenance tasks.
Screenshot
Manufacturing Master Management
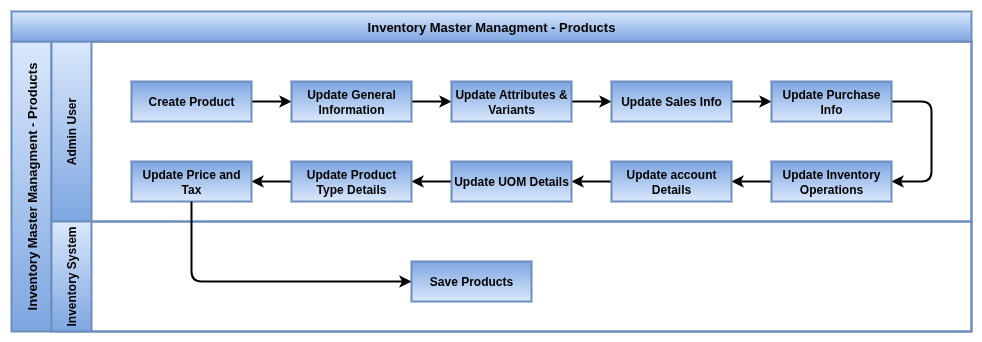
Products
Overview
Odoo Inventory is a modern, scalable solution designed to optimize warehouse management and stock control. With advanced features like multi-warehouse support, real-time product tracking, automated replenishment, and deep integration with Odoo’s sales, purchase, and manufacturing apps, it empowers businesses to maintain accurate inventory, reduce stock outs, and improve fulfillment speed and accuracy.
Process Flow
Business Rules
- Only products marked as Stockable are tracked with real-time quantity updates in the inventory system; consumables and services are managed differently.
- Lot and serial number tracking is fully supported, allowing precise traceability from receipt to delivery, essential for compliance and quality control.
- Warehouses are divided into hierarchical locations (aisles, shelves, bins), enabling granular stock management and efficient picking strategies.
- Every stock movement (receipt, delivery, internal transfer) is recorded as a stock move; stock quantities are updated immediately upon validation.
- Replenishment rules can be configured using minimum and maximum stock levels per product and warehouse, automatically triggering purchase orders or manufacturing orders when stock is low.
- Procurement can be set to Make to Order or Buy, allowing flexible sourcing strategies aligned with demand and supply conditions.
- Odoo supports automated barcode scanning and IoT device integration to streamline warehouse operations and reduce manual errors.
- Regular inventory adjustments and cycle counts ensure stock accuracy, with variance tracking and detailed audit logs.
- Role-based access rights and approval workflows safeguard inventory integrity, restricting sensitive operations to authorized personnel.
- Complete audit trails provide full visibility into stock movements and user actions for regulatory compliance and operational transparency.
Screenshot
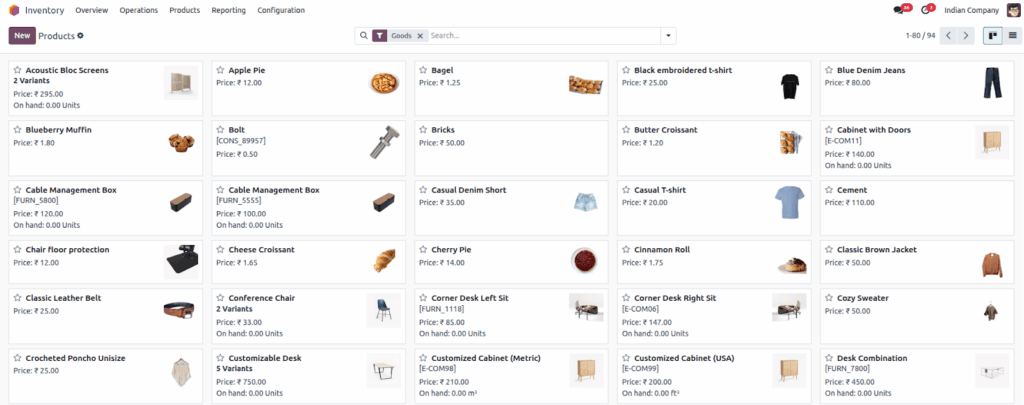
Product Variants
Overview
Manage products with multiple variants efficiently. Whether it’s different sizes, colors, or other attributes, product variants help you offer a wide range of options without creating separate products for each variation. This keeps your inventory organized and simplifies stock tracking and sales processes.
Process Flow
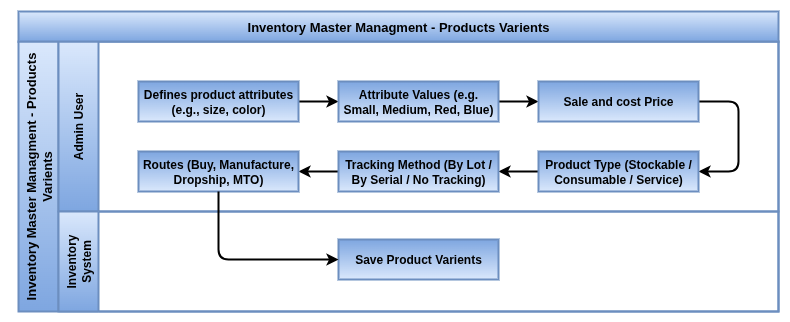
Business rules
- Products can have multiple attributes (e.g., size, color, material), and each unique combination forms a variant.
- Variants are treated as individual stockable items with their own SKU, barcode, price, and inventory levels.
- You can configure attribute values to affect cost, price, and availability at the variant level.
- Variants can be managed across multiple warehouses and locations with accurate stock tracking.
- The system supports variant-specific barcodes and serial numbers, enabling precise identification and traceability.
- Sales, purchase, and manufacturing processes seamlessly handle variants, ensuring correct variant selection at every step.
- Variants simplify catalog management by consolidating all options under a single product template, reducing duplication.
- Variant rules and filters can be used in reporting and replenishment, enabling granular inventory control.
Screenshot
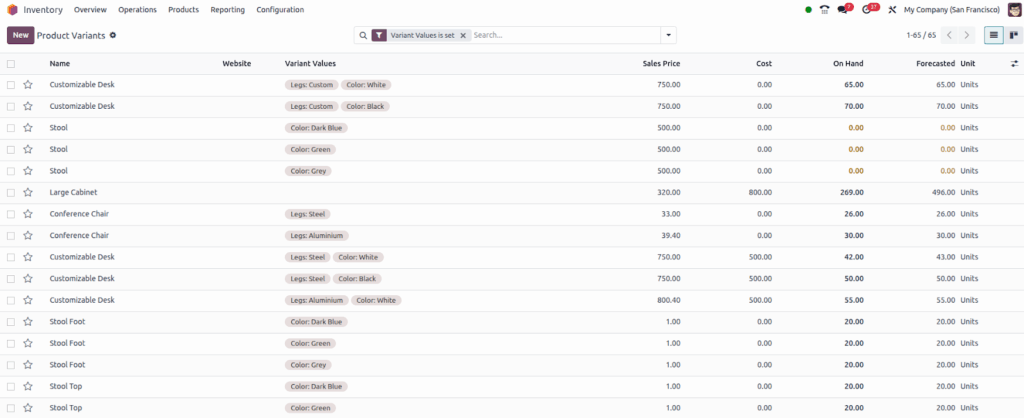
Bill of Materials (BoM)
Overview
In Odoo 18 Enterprise Manufacturing, a Bill of Materials (BoM) defines the list of components, sub assemblies, and operations needed to manufacture a product. It acts as the central structure that guides production planning, execution, and cost tracking. BoMs ensure consistency in production by detailing what is needed, in what quantity, and in what sequence. They also support advanced scenarios such as product variants, multi-level assemblies, by-products, and subcontracted operations, making them highly flexible for complex manufacturing setups.
Process Flow
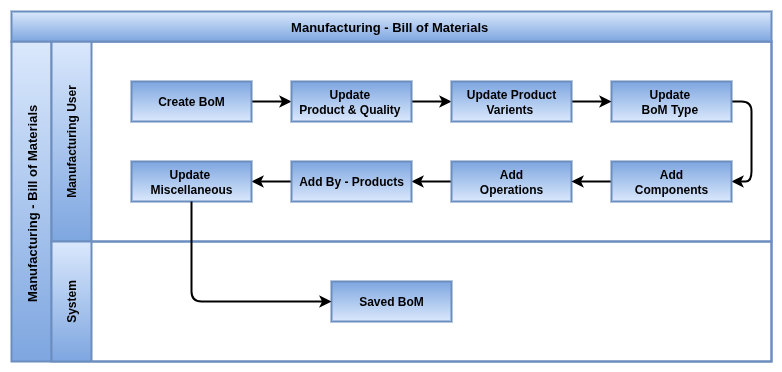
Business Rules
- A BoM is required for any product that is to be manufactured through a manufacturing order.
- Only one BoM can be set as the default for each product; additional BoMs can be configured for variants or alternative production methods.
- BoMs can be associated with specific product variants to manage unique component structures per variant.
- Sub assemblies can be managed using multi-level BoMs where components themselves have their own BoMs.
- When a routing is linked to a BoM, Odoo automatically generates work orders for each defined operation during production.
- Operations can be scheduled to specific work centers and include setup time, duration, cleanup time, and labor costing.
- By-products can be defined in the BoM and are automatically tracked during production, allowing for reuse, storage, or sale.
- Component quantities are specified for a given production quantity (usually per 1 unit), with support for unit of measure conversion.
- The BoM supports different types such as manufacturing, kits (used for sales kits), and subcontracting.
- Subcontracted BoMs send raw materials to vendors and receive finished goods as part of external manufacturing flows.
- The cost of a BoM is calculated based on materials, operations, labor, subcontracting, and overheads, contributing to the total cost of the finished product.
- BoMs support configurable consumption methods—materials can be consumed automatically or require manual validation.
- A BoM must be active and properly defined for a manufacturing order to be confirmed; errors or missing configurations will block the order.
- During the manufacturing process, Odoo performs a BoM explosion to determine the full list of required components and sub assemblies.
- Versioning is not managed natively but multiple BoMs can be created with unique names or references to simulate version control.
- Products must be correctly configured with the “Manufacture” route and a valid BoM to be planned through MRP.
- If no routing is defined, manufacturing orders are created without work orders, treating the production as a single step.
- Cost structure analysis and reporting rely on accurate BoM data, as it’s used in production costing, margin analysis, and forecasting.
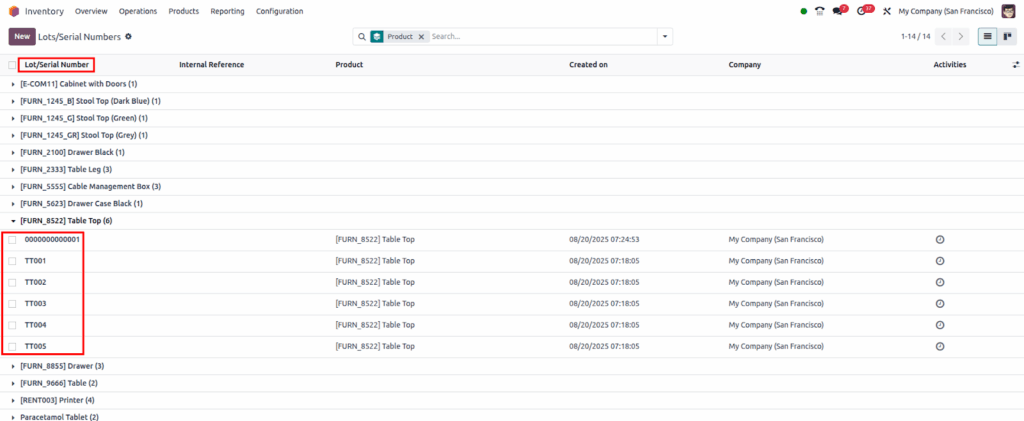
Lots and Serial Numbers
Overview
Odoo offers robust lot and serial number management to ensure complete traceability and control over your inventory. Whether you need batch tracking for quality control, expiry dates, or unique serial tracking for warranty and service, Odoo lets you handle all these requirements seamlessly.
Process Flow
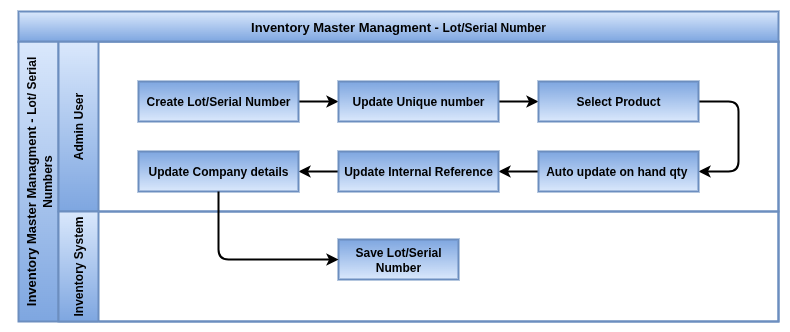
Business Rules
- Lot Numbers group products in batches, allowing you to track production runs, expiration dates, and quality checks.
- Serial Numbers provide unique identifiers for individual items, essential for warranty management, repairs, and after-sales support.
- Lot and serial number tracking can be enabled per product, depending on the business need.
- Every stock move (receipt, internal transfer, delivery) records the lot or serial numbers involved, ensuring precise traceability.
- Integration with barcode scanners supports quick scanning of lot and serial numbers during warehouse operations.
- You can configure lot expiration dates, and Odoo can automatically alert you to products nearing expiry to reduce waste.
- Traceability reports allow tracking the history of a lot or serial number from supplier to customer, including manufacturing, storage, and sales data.
- Serial and lot numbers can be used in quality control workflows, enabling inspections and blocking defective batches or items.
- User access controls restrict who can assign or modify lot and serial numbers to maintain data integrity.
Screenshot
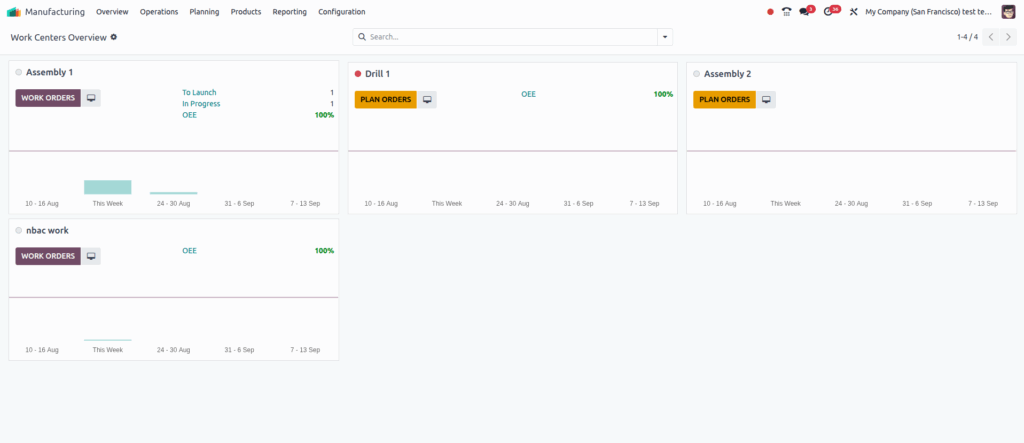
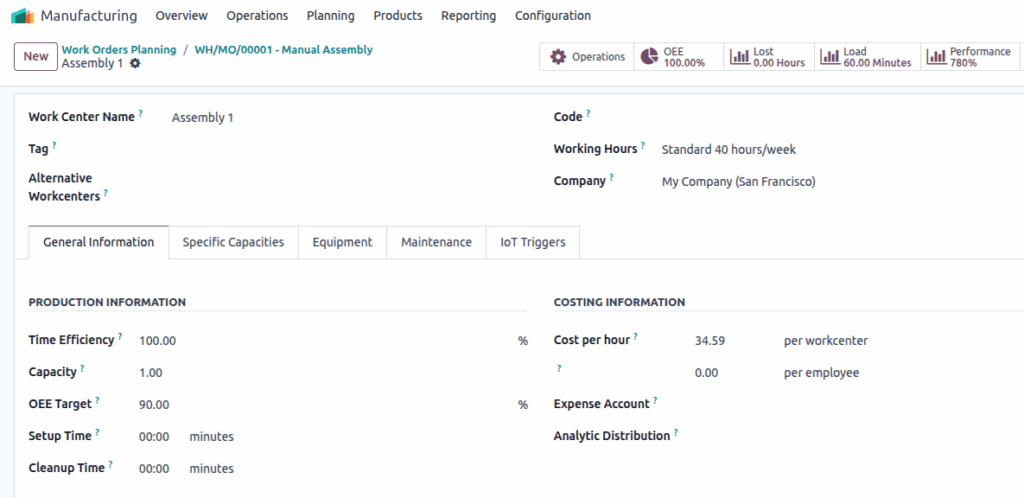
Work Centers
Overview
Work centers are specific locations where manufacturing work orders are executed. They enable tracking of production capacity, scheduling, costs, and efficiency. Each work center operates within defined working hours, which impact scheduling and performance metrics like Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). Work centers can have assigned employees and equipment, and support multiple shifts through duplicated configurations.
Process Flow
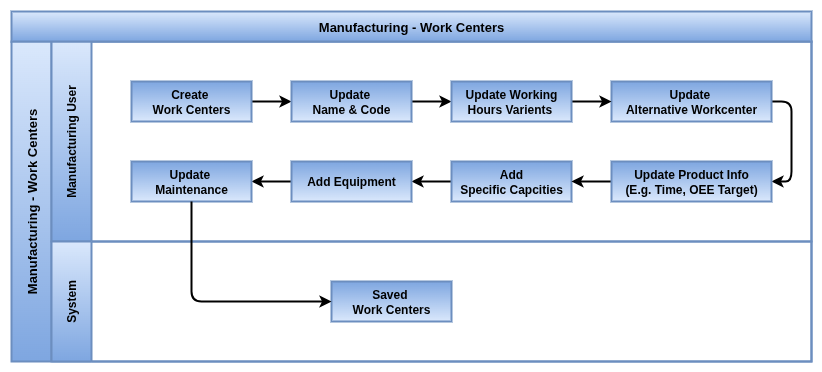
Business Rules
- Work centers must be enabled by activating the Work Orders setting in Manufacturing Configuration before use.
- A work center is mandatory when defining operations in a Bill of Materials (BoM).
- Each work center has configurable attributes: name, code, tags, alternative work centers, working hours, capacity, setup and cleanup times, cost per hour, and allowed employees.
- Working hours can be customized and form the basis for calculating efficiency metrics like OEE.
- Capacity can be set globally or per product basis.
- Employees assigned to a work center must have the necessary qualifications or certifications if restrictions are applied.
- IoT device integration is supported to automate or monitor equipment actions within a work center.
- Work centers support multiple shifts by creating duplicate centers with distinct working hours.
- Work orders are scheduled and tracked by work center, with real-time performance metrics available for analysis.
- Alternate work centers can be specified for fallback during unavailability.
- Work centers help in organizing and planning manufacturing processes to maximize productivity and cost efficiency.
Screenshot
Operations
Overview
Operations represent the fundamental tasks or steps in the manufacturing process. Each operation is tied to a specific work center where the actual production activity takes place. Operations define the required duration, resources, and instructions needed to complete a manufacturing task. They are essential components in the Bill of Materials (BoM) and work orders, guiding production workflows and scheduling.
Process Flow
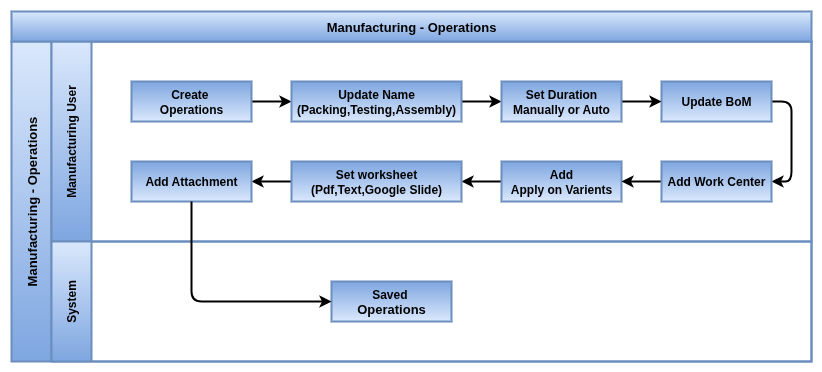
Business Rules
- Work Center Assignment: Every operation must be linked to a designated work center where the task is executed.
- Duration Management: Operation duration can be manually set or automatically computed based on tracked work time, enabling accurate scheduling and time tracking.
- Resource Allocation: Operations specify employee capacity and may restrict execution to authorized personnel with required skills or certifications.
- Instructions and Worksheets: Work instructions or customizable worksheets can be attached to operations to ensure consistent quality and process adherence.
- Sequencing and Dependencies: Operations can be sequenced with dependencies to enforce the correct order of manufacturing steps.
- Applicability: Operations can apply to all product variants or specific variants to support customized manufacturing routes.
- Integration with Manufacturing Orders: Operations form the backbone of work orders, driving the manufacturing process from planning through execution.
- These are common operation types configured in the manufacturing process within Odoo: Manual Assembly, Packing, Testing, Long Time Assembly, Quality Inspection, Machine Setup, Painting, Welding, Drilling, Final Assembly
Screenshot
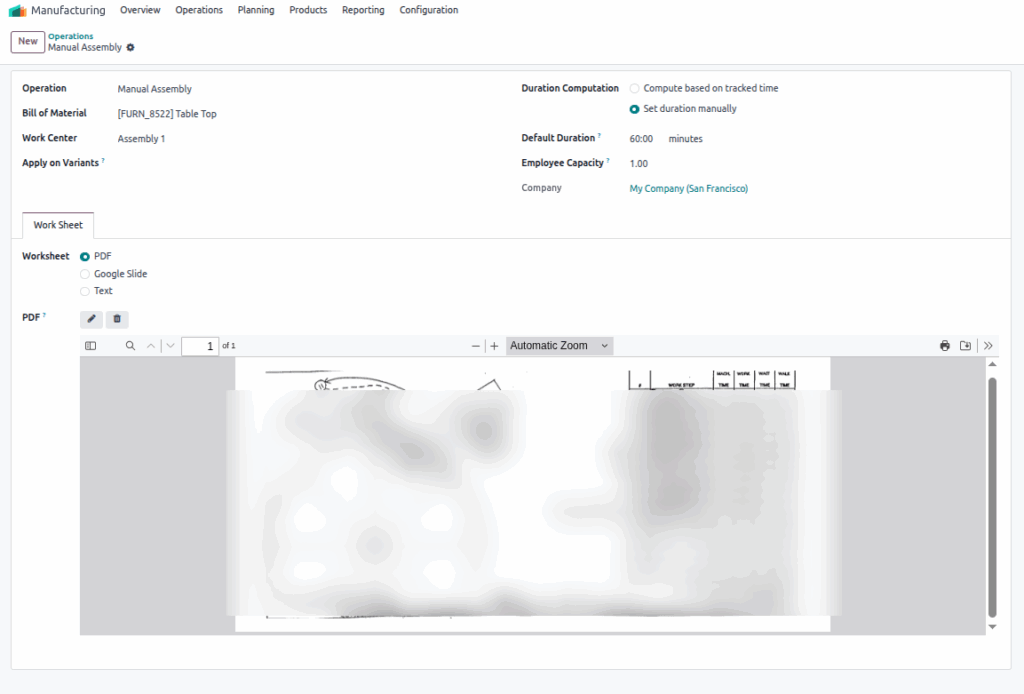
Manufacturing Operations Management
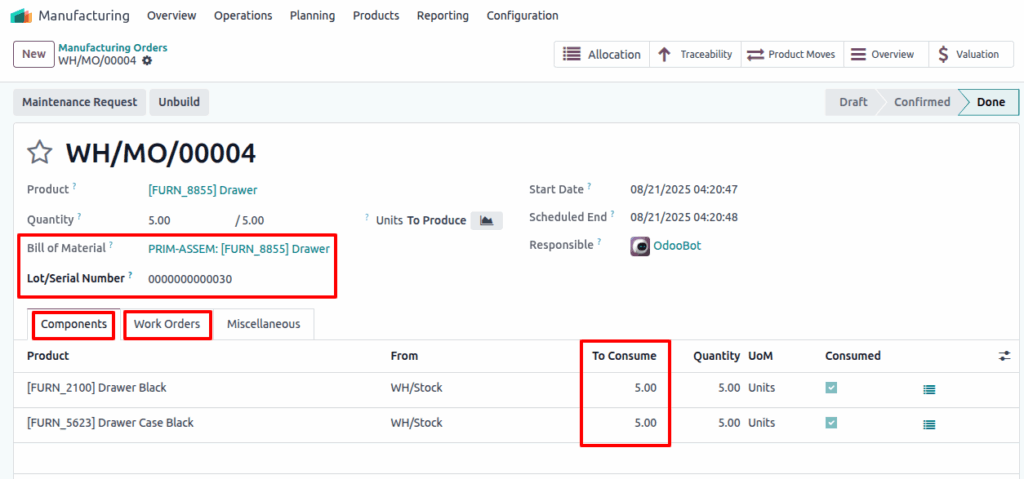
Manufacturing Orders (MOs)
Overview
Manufacturing Orders in Odoo control the production of finished goods using predefined Bills of Materials (BoMs). They form the foundation of the production workflow, integrating planning, materials, routing, and cost control into a unified process.
Process Flow
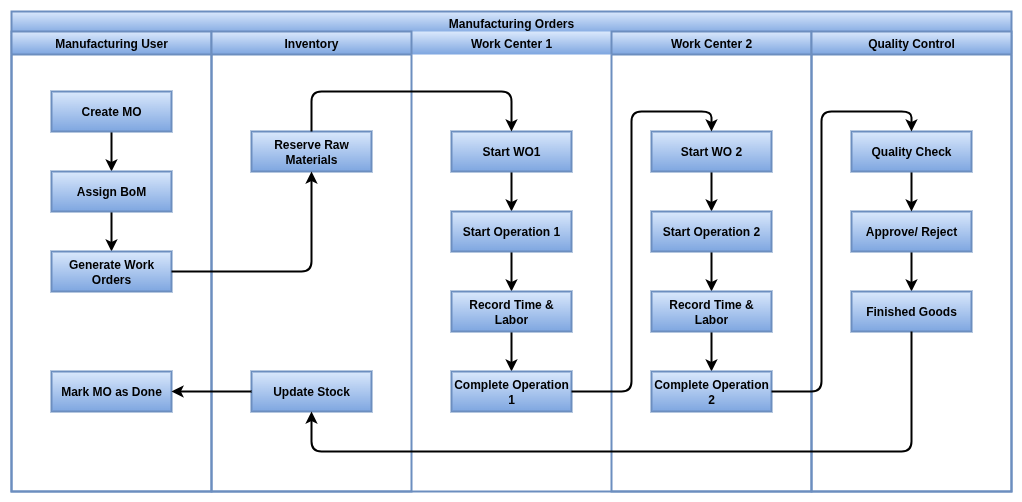
Business Rules
- A product must be configured with the “Manufacture” route to appear in production workflows.
- A valid BoM is required to create and confirm a Manufacturing Order.
- Only one default BoM is allowed per product, but multiple alternate BoMs can exist for variants.
- An MO cannot be confirmed without a BoM and either available stock or active procurement rules.
- Odoo reserves materials automatically upon MO confirmation.
- If materials are not available, purchase or transfer orders are auto-triggered based on defined routes.
- A responsible user (e.g., production manager) must be assigned to each MO for tracking.
- If routing is included in the BoM, Work Orders are generated automatically.
- MOs can include planned start dates and deadlines to aid scheduling and capacity planning.
- Manufacturing Orders go through workflow stages: Draft → Confirmed → In Progress → Done → Canceled.
- On completion, raw materials are consumed, and finished goods are added to stock automatically.
- System supports lot and serial tracking of both components and final products.
- Backorders are automatically created if partial production is completed.
- MO completion triggers accounting entries if integrated with real-time inventory valuation.
Screenshot
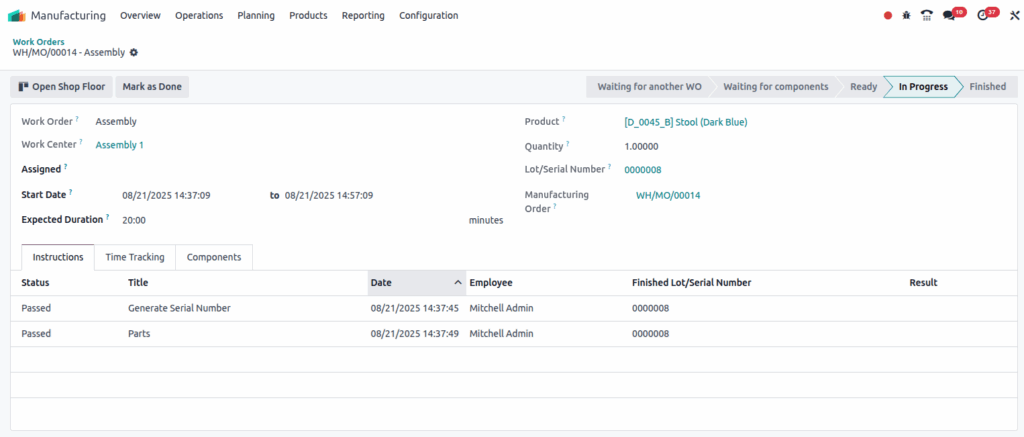
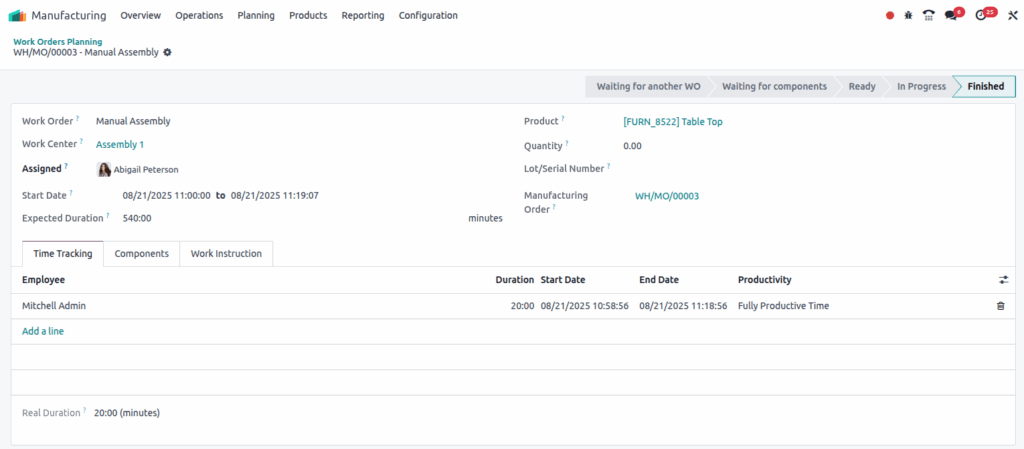
Work Orders (WOs)
Overview
Work Orders represent individual tasks within a Manufacturing Order. Each operation is performed at a designated work center and includes features like time tracking, instructions, quality control, and performance evaluation.
Process Flow
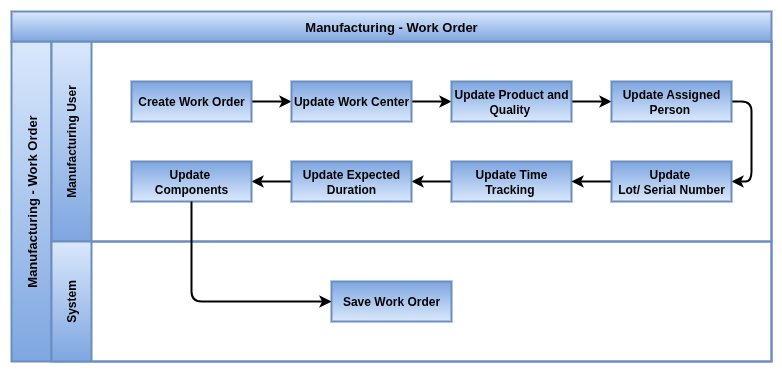
Business Rules
- Work Orders are created only if a routing is linked to the BoM.
- Each operation is assigned to a Work Center, which defines its working schedule and capacity.
- Operations must follow the sequence defined in the routing, unless set as parallel operations.
- A Work Order cannot be started unless all required raw materials are reserved or manually forced.
- Work Orders allow operator instructions, which can include documents, checklists, or manuals.
- Time tracking includes setup time, processing time, and teardown time (if configured).
- Manual or automated quality checks can be added at any operation step.
- If a product fails quality checks, the operator can mark it as scrap or hold for inspection.
- Downtime reasons (e.g., machine failure, material shortage) can be recorded in the WO interface.
- Performance data is used to calculate OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) metrics.
- Users must manually Start → Pause → Resume → Mark Done for each Work Order.
- Each operation can have an associated cost per hour, affecting total production cost.
- Completion of all Work Orders automatically completes the parent MO.
Screenshot
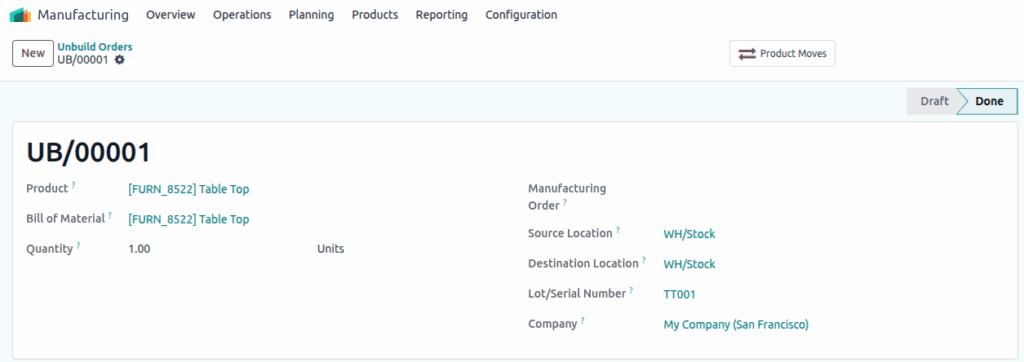
Unbuild Orders
Overview
Unbuild Orders allow the reverse manufacturing process — breaking down finished goods into their original components. This feature is useful for quality failures, rework, or salvage operations.
Process Flow
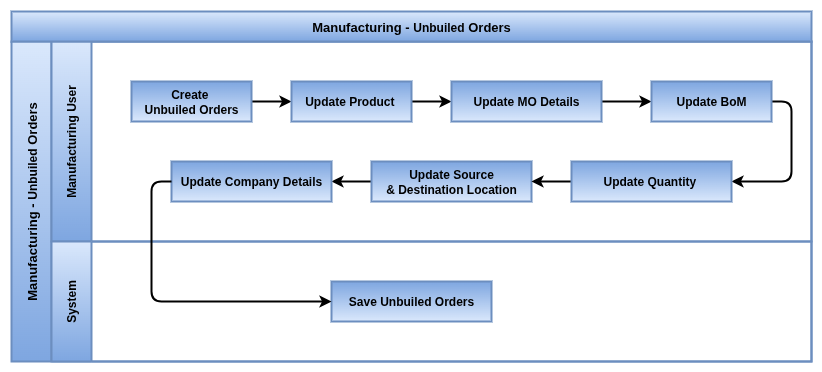
Business Rules
- Products must be stockable to be eligible for unbuilding.
- Unbuild Orders can be linked to a specific MO or use a generic BoM.
- Supports lot/serial numbers to ensure component traceability.
- Upon validation:
- The finished product is removed from stock.
- The components are added back to inventory based on the BoM structure.
- If the MO or BoM uses byproducts, those can be reintroduced during unbuilding.
- Can be used for internal quality handling, product returns, or rework purposes.
- Costing and inventory adjustments are automatically handled based on valuation method.
- Unbuild Orders are traceable via Inventory Moves and Reporting Logs.
- Only users with proper manufacturing and inventory access rights can perform unbuild operations.
- No routing or operations are required to perform unbuilding.
Screenshot
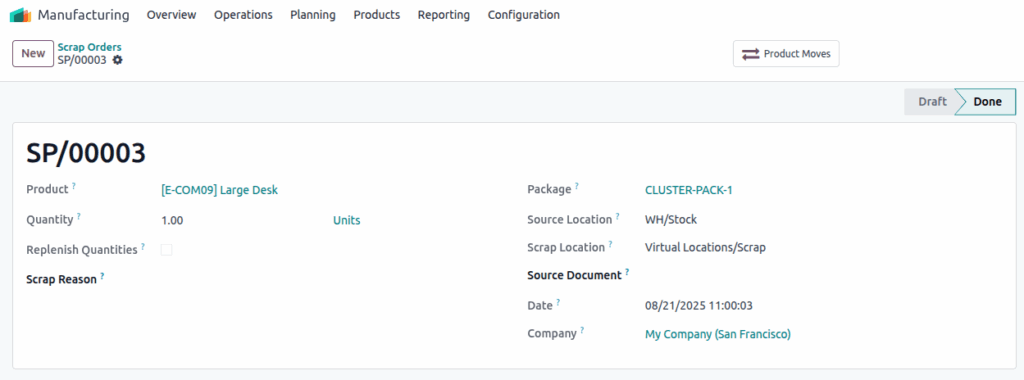
Scrap
Overview
Scrap Orders record damaged, defective, or lost materials during production or inventory operations. Scrapping ensures that unusable products are properly separated and accounted for in stock and cost records.
Process Flow
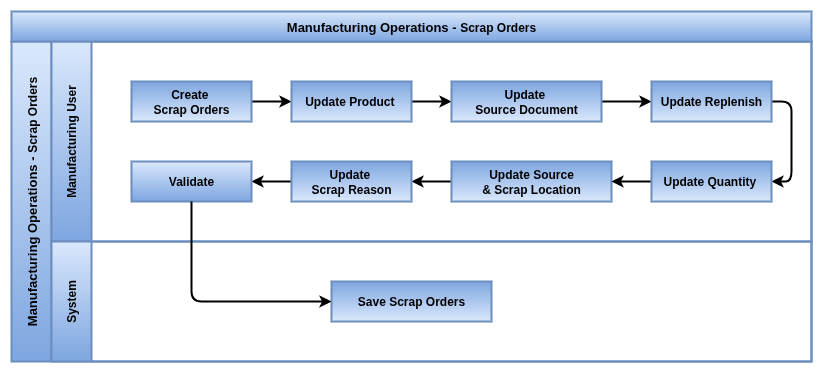
Business Rules
- Scrap can be initiated from:
- Manufacturing Orders
- Work Orders
- Inventory locations
- Scrapped items are moved to a Scrap Location configured in the system.
- Scrap locations are excluded from available stock for operations and sales.
- Scrapping can be done for:
- Raw materials
- Work-in-progress items
- Finished goods
- Users can define scrap reasons (e.g., defective part, excess material, test failure).
- Each scrap action is logged in the stock move history for traceability.
- Scrapping a product does not automatically adjust the MO or WO quantity unless manually updated.
- If lot/serial tracking is enabled, scrapped items must be properly assigned to a tracked unit.
- Scrap quantity cannot exceed available stock at the time of scrapping.
- Scrap entries are reflected in valuation layers for accurate cost accounting (if accounting is integrated).
- Scrap reports can be filtered by date, product, reason, and responsible user.
Screenshot
Manufacturing Planning Management
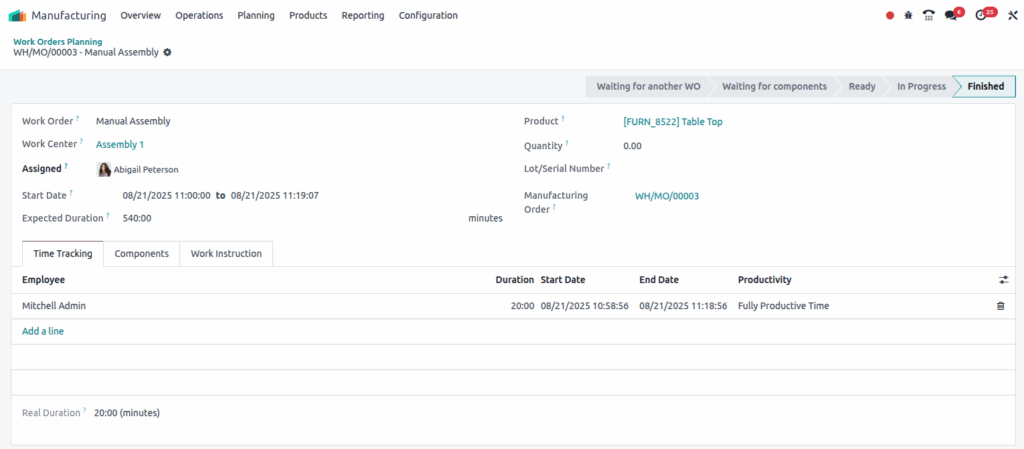
Planning By Production
Overview
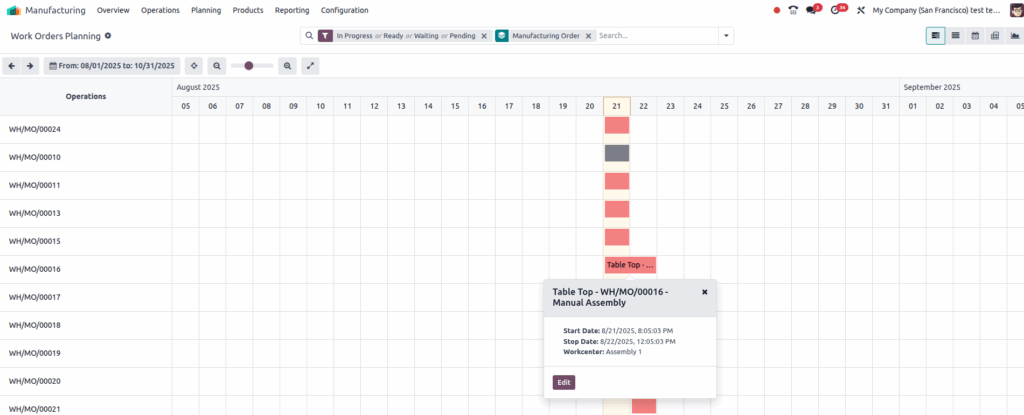
Planning by Production in Odoo provides a clear, order-focused view of all Work Orders grouped under each Manufacturing Order (MO). It helps production managers schedule and monitor the sequence of operations needed to complete a product, ensuring deadlines are met and resources are optimized. This view supports real-time adjustments and integrates material availability and time tracking for smooth manufacturing workflows.
Process Flow
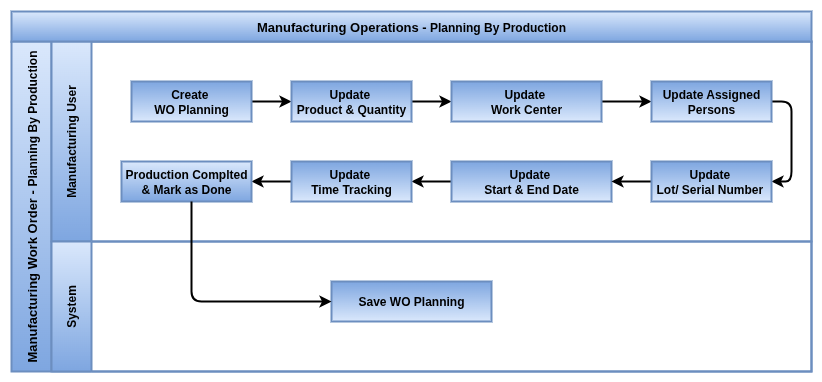
Business Rules
- Work Orders are grouped under their Manufacturing Order, providing a unified view of all operations needed for product completion.
- Every Work Order corresponds to an operation defined in the routing of the Manufacturing Order’s Bill of Materials (BoM).
- Each Work Order is linked to a specific Work Center, which is assigned automatically based on routing settings.
- The quantity of product to manufacture is set at the MO level and applies uniformly across all related Work Orders.
- Planned start and end dates for each Work Order must respect the assigned Work Center’s calendar, including working hours and holidays.
- The expected duration of each Work Order is derived from routing operation time, adjusted for the production quantity and Work Center efficiency.
- If product tracking is enabled, the Lot or Serial Number must be specified for traceability.
- Operators can log the real duration spent on each operation, either manually or automatically if IoT devices are integrated.
- Work instructions are linked to each Work Order to provide operators with necessary guidance and documentation.
- All required components must be reserved and available before a Work Order can be started; otherwise, manual override is required.
- Work Orders must be performed in the sequence defined in the routing, with subsequent operations dependent on the completion of prior ones.
- Users with appropriate access rights can reschedule Work Orders by adjusting their planned dates within the interface.
- Once a Work Order is completed, it becomes locked to prevent further changes.
- Rescheduling a Work Order updates the overall Manufacturing Order timeline to reflect new production deadlines.
- Time tracking and component consumption data feed into production analytics, enabling performance measurement and continuous improvement.
- The system automatically synchronizes planning adjustments with inventory levels, ensuring material availability aligns with production schedules.
Screenshot
Dashboard
Planning by Work Center
Overview
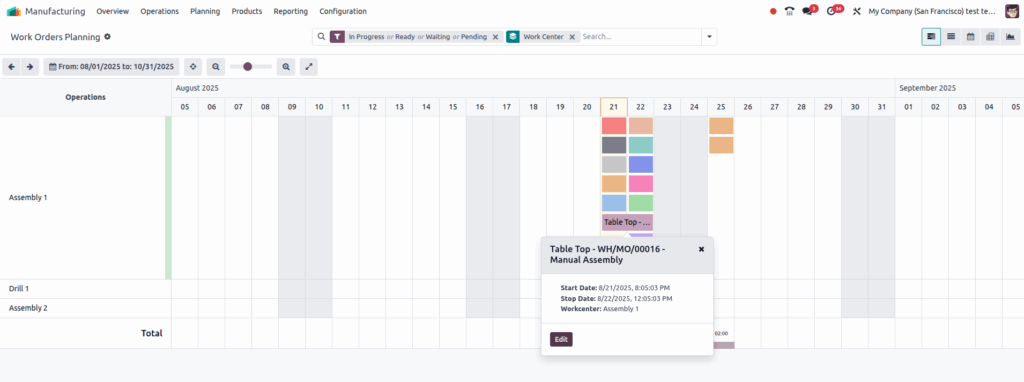
Work center planning in Odoo allows you to view and manage all scheduled work orders by work center. Using the Manufacturing app’s Planning module, you can see a Gantt chart that visualizes how work orders are distributed across work centers over time. This helps monitor production load, schedule tasks efficiently, and adjust work order timings or assignments directly from the planning interface.
Business Rules
- Work orders are assigned to specific work centers based on the operations defined in the Bill of Materials (BoM).
- Scheduling is visualized in a Gantt view, showing work order duration and timing by work center.
- Users can modify work order start times and change assigned work centers from the planning view.
- The planning tool helps balance workload by showing how many minutes per hour each work center is occupied.
- Accurate planning requires properly configured working hours for each work center.
- Planned schedules should consider capacity, setup, and cleanup times to avoid overbooking work centers.
Screenshot
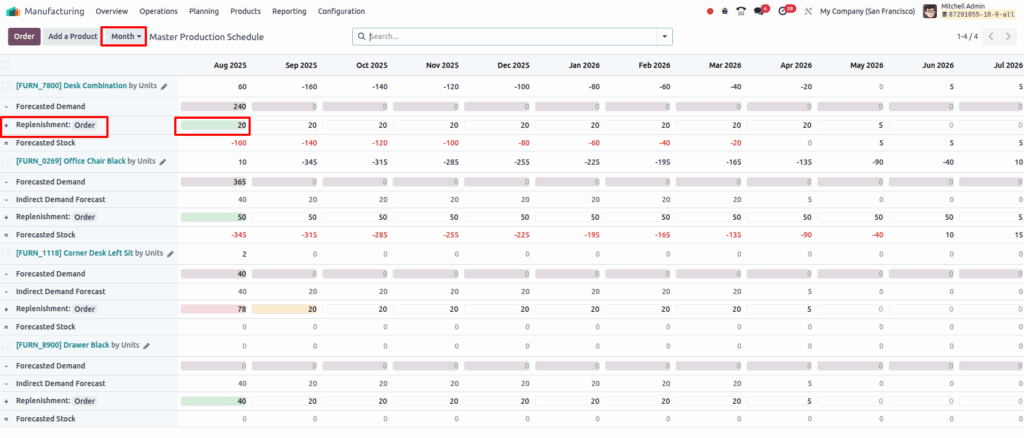
Master Production Schedule
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) in Odoo is a manual planning tool that helps manage manufacturing and purchase orders based on forecasted demand. It enables businesses to proactively plan product replenishment by considering current orders and future demand, ensuring optimal stock levels and smooth production flow.
Business Rules
- MPS requires manual input and adjustments; it does not generate orders automatically without confirmation.
- Manufactured products must have the “Manufacture” route enabled; purchased products must have the “Buy” route set with vendor and pricing details.
- Forecasted demand is entered manually or derived from historical data and sales trends for each period.
- Indirect demand reflects component needs driven by manufacturing orders of finished products via Bills of Materials.
- Suggested replenishment quantities are calculated considering demand, current stock, safety stock targets, and min/max replenishment limits but can be edited by planners.
- Forecasted stock shows projected inventory levels after demand and replenishment, helping identify shortages or surpluses.
- Replenishment status is visually indicated by color codes signaling urgency or overstock conditions.
- Replenishment orders are generated only upon manual confirmation, creating manufacturing orders or purchase requests accordingly.
- Products can be replenished individually, in groups, or all at once through bulk actions.
- Safety stock targets set minimum stock levels to avoid stockouts.
- Minimum and maximum replenishment settings ensure efficient ordering quantities.
- Adding a product with a Bill of Materials includes its components in the schedule automatically, but components can be managed independently if desired.
- Multi-warehouse environments allow specifying which warehouse to replenish.
- Products can be edited or removed from the MPS as needed, with changes saved for ongoing planning.
- Only authorized users with appropriate permissions can modify schedules or confirm replenishment orders.
- All orders generated through MPS link back to it for clear traceability and auditability.
Screenshot
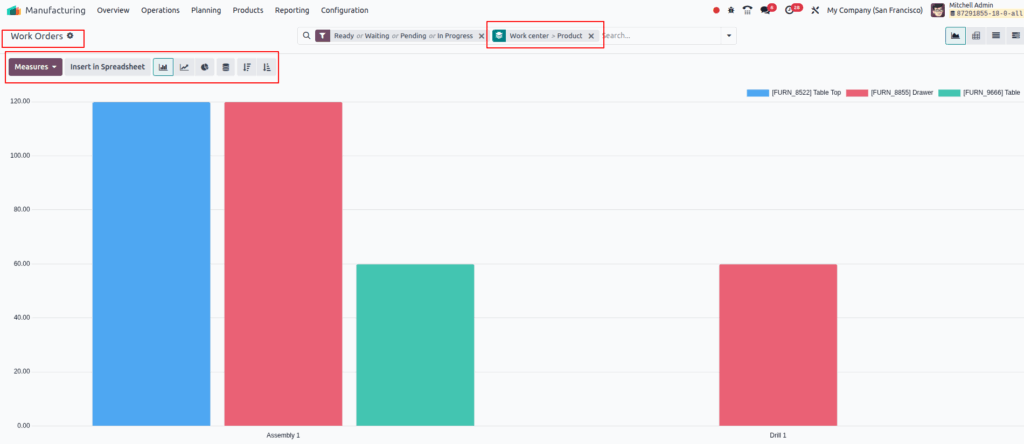
Work Orders
Overview
Odoo Manufacturing offers powerful reporting dashboards that provide real-time insights into production performance. These dashboards consolidate data from various modules like Work Orders, Work Centers, and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), enabling managers to monitor key metrics, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to optimize manufacturing operations.
Business Rules
- Dashboards aggregate data from multiple manufacturing sources such as work orders, work centers, and production schedules.
- Users can customize dashboards by selecting relevant metrics and timeframes.
- Visualizations include bar charts, pie charts, line charts, pivot tables, and lists for flexible analysis.
- Dashboards update dynamically with real-time production data.
- Filtering options allow users to drill down by work center, product, date range, or shift.
- Reports can compare performance across shifts, products, and work centers.
- Access to dashboard views is role-based to ensure data security.
- Dashboards support export and sharing options for collaboration.
Screenshot
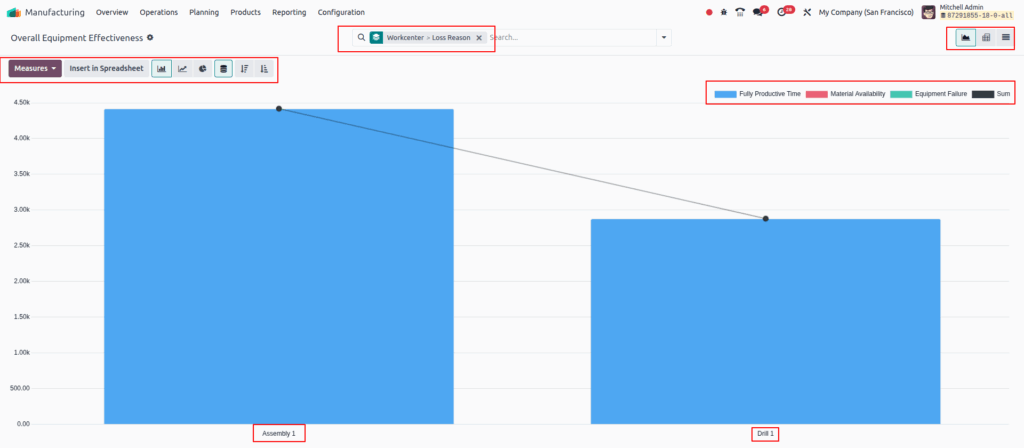
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Overview
OEE Reporting in Odoo provides detailed insights into equipment effectiveness for each work center. Users can access comprehensive OEE metrics via visual charts or data views, enabling real-time monitoring of production efficiency. The reporting interface supports multiple visualization formats, including bar, pie, and line charts, as well as pivot and list views for detailed analysis. This flexibility helps manufacturing managers quickly identify performance gaps and optimize resource utilization.
Business Rules
- OEE metrics can be viewed globally for all work centers or individually per work center.
- Access overall OEE reports via Manufacturing app ‣ Reporting ‣ Overall Equipment Effectiveness.
- Access individual work center OEE reports from Manufacturing app ‣ Configuration ‣ Work Centers, using the OEE smart button on the work center form.
- Users can switch between bar chart, line chart, and pie chart visualizations for better data interpretation.
- Pivot and list views are available for detailed time-entry data and granular analysis.
- Only validated and completed Work Orders contribute data to the OEE calculations and reports.
- OEE reporting relies on accurate time tracking and production data entered during Work Order processing.
- The system updates OEE metrics automatically as new data becomes available, supporting continuous performance monitoring.
Screenshot
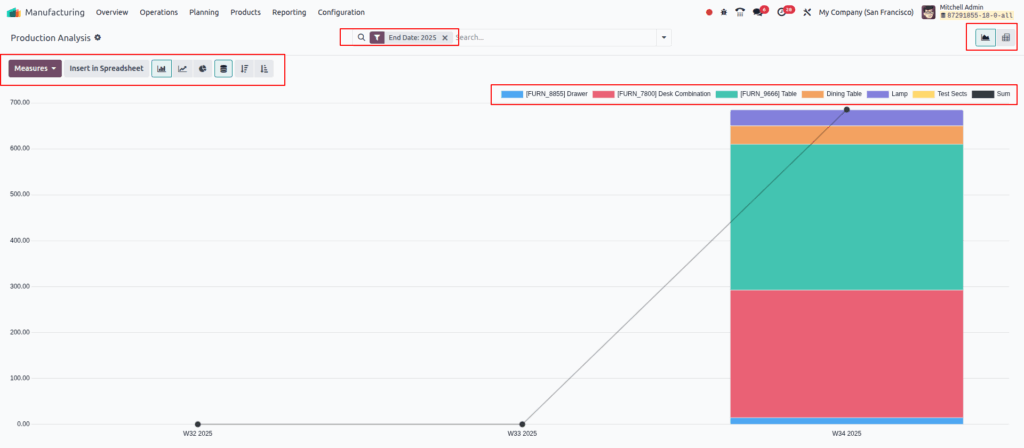
Production Analysis
Overview
The Production Analysis report in Odoo Manufacturing provides essential statistics on manufactured products, including production costs, operation duration, and quantities produced. It helps manufacturers understand cost drivers, evaluate product efficiency, and monitor overall production performance. The report supports data visualization through charts and pivot tables, enabling comparisons across products and time periods.
Business Rules
- The report measures key metrics such as average cost per unit, total cost, operation duration, employee and subcontractor costs, and yield percentage.
- Only one measure can be selected at a time in graph views; multiple measures are supported in pivot view.
- Users can filter and group data by product, date range, and other criteria for detailed analysis.
- Comparison feature allows contrasting two different time periods or sets of products.
- Products must be included in manufacturing orders (MOs) to appear in the report.
- Data accuracy depends on correctly recorded MO details and cost entries.
- Use cases include identifying costly products for discontinuation or comparing production costs across quarters.
Screenshot
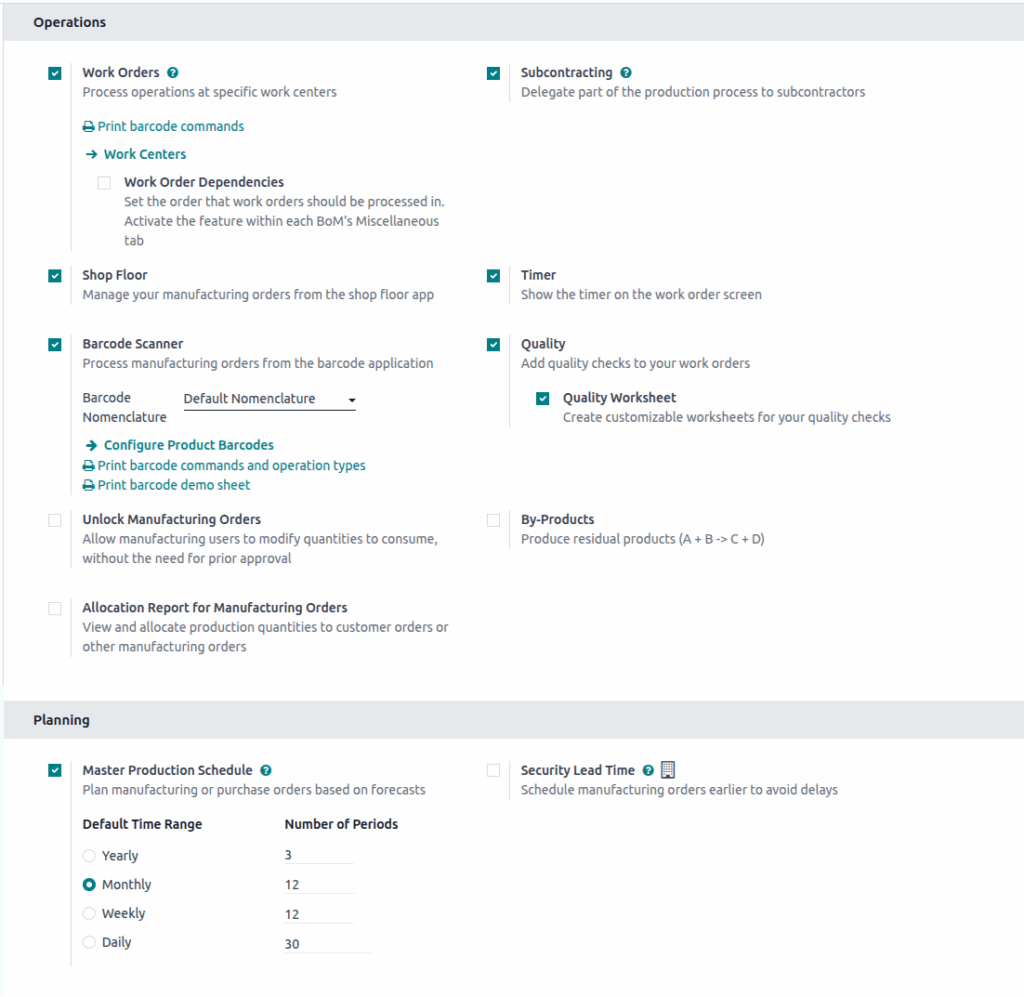
Manufacturing Configuration Settings
Overview
Customize and control your production operations with flexible configuration options designed to optimize efficiency, quality, and resource planning. These settings enable powerful capabilities across the shop floor, work centers, forecasting, and more.
Configuration Settings
Work Orders
- Work orders are enabled per routing and triggered when linked to a BoM.
- Required to process production in discrete operations across work centers.
- Each work order corresponds to a specific step in the routing.
Work Order Dependencies
- Dependencies must be defined within the BoM under the “Miscellaneous” tab.
- Work orders will not be activated unless predecessor steps are completed.
- Ensures correct operational flow (e.g., painting only after assembly).
Subcontracting
- Allows outsourcing of specific operations to third-party vendors.
- Requires a BoM of type “Subcontracting” and vendor configuration.
- Raw materials are delivered to the subcontractor; finished goods are received in return.
- Traceability and costing are tracked automatically.
Shop Floor
- Enables real-time production control through a dedicated interface.
- Operators can view and manage manufacturing orders directly from the shop floor screen.
- Reduces reliance on paper instructions or external communication.
Timer
- Displays a live timer on work order screens.
- Helps monitor actual operation duration and time efficiency.
- Time data is used in OEE and cost calculations.
Barcode Scanner
- Manufacturing operations can be processed using barcodes.
- Supports scanning to start, pause, and finish work orders.
- Improves speed and accuracy in shop floor execution.
Barcode Nomenclature
- Standardizes barcode formats across operation types.
- Required for proper decoding in barcode-based workflows.
- Includes demo sheets and templates for testing.
Quality
- Enables quality checkpoints on work orders.
- Checks can be automatic, conditional, or manual.
- Results are logged for traceability and compliance.
Quality Worksheet
- Provides operators with a form or checklist during production.
- Can include pass/fail checks, numeric measurements, or observations.
- Fully customizable per work center or operation.
Unlock Manufacturing Orders
- Allows production operators to adjust consumed quantities directly.
- No approval required if setting is active.
- Helps accommodate real-world variations in raw material usage.
By-Products
- Supports production of secondary outputs from a single process.
- All by-products must be defined in the BoM.
- Quantities can be fixed or variable per production.
Allocation Report for Manufacturing Orders
- Shows where finished products are allocated (e.g., customer orders).
- Helps in prioritizing production based on demand.
- Links MO planning with delivery commitments.
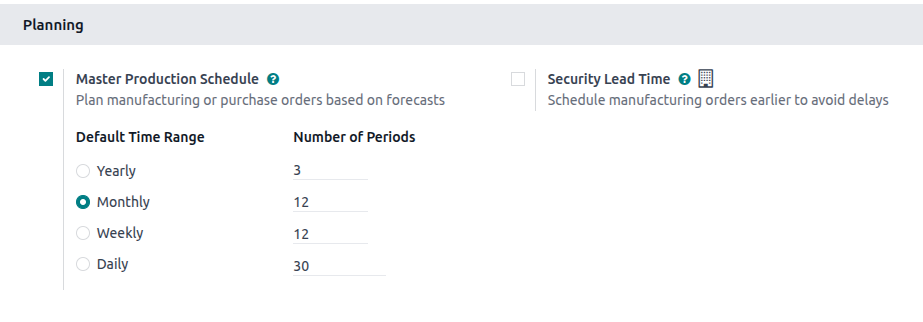
Planning – MPS
Master Production Schedule
- Provides forecast-based production and purchasing planning.
- Allows manual or semi-automated planning based on expected demand.
- Can consider forecasted sales, actual demand, and safety stock.
Default Time Range
- Determines the granularity of MPS (e.g., weekly, monthly).
- Helps align planning with business cycles.
Number of Periods
- Defines how many future periods (columns) are visible in MPS.
- Useful for long-term production visibility.
Security Lead Time
- Adds a buffer to manufacturing dates to prevent delays.
- Helps ensure production is completed before due dates.
- Configurable per product or globally in the settings.
Screenshot